Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00390) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Ticarcillin/Clavulanic acid
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Ticarcillin-clavulanic acid; 86482-18-0; BRL 28500; Clavulanic acid mixture with Ticarcillin; (2S,5R,6R)-6-[[(2R)-2-carboxy-2-thiophen-3-ylacetyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid;(2R,3Z,5R)-3-(2-hydroxyethylidene)-7-oxo-4-oxa-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid; Clavulanic acid - ticarcillin mixt.; Ticarcillin - clavulanic acid mixt.; BRL-28500; Ticarcillin disodium and clavulanate potassium; Ticarcillin-clavulanic acid mixt.; TIMENTIN IN PLASTIC CONTAINER; TICAR & CA; Clavulanic acid & Ticarcillin; Ticarcillin & Clavulanic acid; Ticarcillin and clavulanic acid; SCHEMBL1650350; CHEMBL3137696; DTXSID10235588; 4-Oxa-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic acid, 3-(2-hydroxyethylidene)-7-oxo-, (2R,3Z,5R)-, mixt. with (2S,5R,6R)-6-(((2R)-carboxy-3-thienylacetyl)amino)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic acid; 4-Oxa-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic acid, 3-(2-hydroxyethylidene)-7-oxo-, (2R-(2-alpha,3Z,5-alpha))-, mixt. with (2S-(2-alpha,5-alpha,6-beta(S*)))-6-((carboxy-3-thienylacetyl)amino)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic acid; Timentin (Ticarcillin disodium/Clavulanate potassium); (2R,3Z,5R)-3-(2-hydroxyethylidene)-7-oxo-4-oxa-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid; (2S,5R,6R)-6-[[(2R)-3-hydroxy-3-oxo-2-(3-thienyl)propanoyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid; 4-Oxa-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic acid, 3-(2-hydroxyethylidene)-7-oxo-, (2R-(2-alpha,3Z,5-alpha))-, & (2S-(2-alpha,5-alpha,6-beta(S*)))-6-((carboxy-3-thienylacetyl)amino)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic acid
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
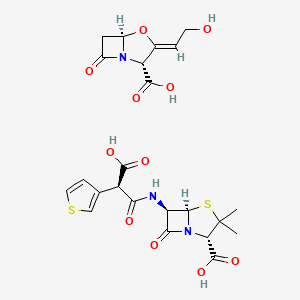
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C23H25N3O11S2
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC1([C@@H](N2[C@H](S1)[C@@H](C2=O)NC(=O)[C@@H](C3=CSC=C3)C(=O)O)C(=O)O)C.C1[C@@H]2N(C1=O)[C@H](/C(=C/CO)/O2)C(=O)O
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C15H16N2O6S2.C8H9NO5/c1-15(2)9(14(22)23)17-11(19)8(12(17)25-15)16-10(18)7(13(20)21)6-3-4-24-5-6;10-2-1-4-7(8(12)13)9-5(11)3-6(9)14-4/h3-5,7-9,12H,1-2H3,(H,16,18)(H,20,21)(H,22,23);1,6-7,10H,2-3H2,(H,12,13)/b;4-1-/t7-,8-,9+,12-;6-,7-/m11/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
XWMVMWTVLSLJGY-FAJPTIRJSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y104A+p.N110D+p.E175Q+p.S179A |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Acinetobacter baumannii CIP70.10 | 470 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae kP3 | 1290996 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa PU21 | 287 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | K. pneumoniae kP3 was resistant to all Beta-lactams, including carbapenems, and expressed the carbapenem-hydrolyzing Beta-lactamase OXA-181, which differs from OXA-48 by four amino acid substitutions. Compared to OXA-48, OXA-181 possessed a very similar hydrolytic profile. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
