Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00381) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Enacyloxin IIA
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Enacyloxin iia; Q27459995; (1S,3R,4S)-3-{[(2E,4E,6E,8E,10Z,12S,13R,14S,17R,18S,19R,20E)-19-(carbamoyloxy)-11,18-dichloro-13,14,17-trihydroxy-6,12-dimethyl-15-oxotricosa-2,4,6,8,10,20-hexaenoyl]oxy}-4-hydroxycyclohexanecarboxylic acid
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
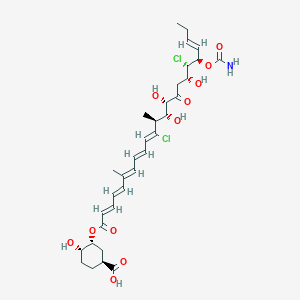
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C33H45Cl2NO11
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC/C=C/[C@H]([C@H]([C@@H](CC(=O)[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](C)/C(=C/C=C/C=C(\\C)/C=C/C=C/C(=O)O[C@@H]1C[C@H](CC[C@@H]1O)C(=O)O)/Cl)O)O)O)Cl)OC(=O)N
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C33H45Cl2NO11/c1-4-5-13-26(47-33(36)45)29(35)24(38)18-25(39)31(42)30(41)20(3)22(34)12-8-6-10-19(2)11-7-9-14-28(40)46-27-17-21(32(43)44)15-16-23(27)37/h5-14,20-21,23-24,26-27,29-31,37-38,41-42H,4,15-18H2,1-3H3,(H2,36,45)(H,43,44)/b8-6+,11-7+,13-5+,14-9+,19-10+,22-12-/t20-,21+,23+,24-,26-,27-,29+,30-,31-/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
IWBADCVFZDCUTN-OCXJTLLTSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Outer membrane porin F (OMPF) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q124K |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain LZ10 | 562 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain LZ33L | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain EV4 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain EV4L | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain LZ12 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain LZ13 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain LZ32 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain LZ34L | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain LZ40L | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain PM816 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | For enacyloxin IIa we discovered four resistant elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu) species in Escherichia coli with the mutations Q124k, G316D, Q329H, and A375T. Among the mutant EF-Tus, three different resistance mechanisms can be distinguished: (i) by obstructing enacyloxin IIa binding to EF-Tu. GTP; (ii) by enabling the release of enacyloxin IIa after GTP hydrolysis; and (iii) by reducing the affinity of EF-Tu.GDP. enacyloxin IIa for aminoacyl-tRNA at the ribosomal A-site, which then allows the release of EF-Tu.GDP.enacyloxin IIa. Ala375 seems to contribute directly to enacyloxin IIa binding at the domain 1-3 interface of EF-Tu.GTP, a location that would easily explain the pleiotropic effects of enacyloxin IIa on the functioning of EF-Tu. | |||
| Key Molecule: Outer membrane porin F (OMPF) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G316D |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain LZ10 | 562 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain LZ33L | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain EV4 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain EV4L | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain LZ12 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain LZ13 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain LZ32 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain LZ34L | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain LZ40L | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain PM816 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | For enacyloxin IIa we discovered four resistant elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu) species in Escherichia coli with the mutations Q124k, G316D, Q329H, and A375T. Among the mutant EF-Tus, three different resistance mechanisms can be distinguished: (i) by obstructing enacyloxin IIa binding to EF-Tu. GTP; (ii) by enabling the release of enacyloxin IIa after GTP hydrolysis; and (iii) by reducing the affinity of EF-Tu.GDP. enacyloxin IIa for aminoacyl-tRNA at the ribosomal A-site, which then allows the release of EF-Tu.GDP.enacyloxin IIa. Ala375 seems to contribute directly to enacyloxin IIa binding at the domain 1-3 interface of EF-Tu.GTP, a location that would easily explain the pleiotropic effects of enacyloxin IIa on the functioning of EF-Tu. | |||
| Key Molecule: Outer membrane porin F (OMPF) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q329H |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain LZ10 | 562 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain LZ33L | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain EV4 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain EV4L | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain LZ12 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain LZ13 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain LZ32 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain LZ34L | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain LZ40L | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain PM816 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | For enacyloxin IIa we discovered four resistant elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu) species in Escherichia coli with the mutations Q124k, G316D, Q329H, and A375T. Among the mutant EF-Tus, three different resistance mechanisms can be distinguished: (i) by obstructing enacyloxin IIa binding to EF-Tu. GTP; (ii) by enabling the release of enacyloxin IIa after GTP hydrolysis; and (iii) by reducing the affinity of EF-Tu.GDP. enacyloxin IIa for aminoacyl-tRNA at the ribosomal A-site, which then allows the release of EF-Tu.GDP.enacyloxin IIa. Ala375 seems to contribute directly to enacyloxin IIa binding at the domain 1-3 interface of EF-Tu.GTP, a location that would easily explain the pleiotropic effects of enacyloxin IIa on the functioning of EF-Tu. | |||
| Key Molecule: Outer membrane porin F (OMPF) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A375T |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain LZ10 | 562 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain LZ33L | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain EV4 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain EV4L | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain LZ12 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain LZ13 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain LZ32 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain LZ34L | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain LZ40L | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain PM816 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | For enacyloxin IIa we discovered four resistant elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu) species in Escherichia coli with the mutations Q124k, G316D, Q329H, and A375T. Among the mutant EF-Tus, three different resistance mechanisms can be distinguished: (i) by obstructing enacyloxin IIa binding to EF-Tu. GTP; (ii) by enabling the release of enacyloxin IIa after GTP hydrolysis; and (iii) by reducing the affinity of EF-Tu.GDP. enacyloxin IIa for aminoacyl-tRNA at the ribosomal A-site, which then allows the release of EF-Tu.GDP.enacyloxin IIa. Ala375 seems to contribute directly to enacyloxin IIa binding at the domain 1-3 interface of EF-Tu.GTP, a location that would easily explain the pleiotropic effects of enacyloxin IIa on the functioning of EF-Tu. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
