Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00325) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Bictegravir
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Bictegravir; 1611493-60-7; GS-9883; UNII-8GB79LOJ07; GS-9883-01; (2R,5S,13aR)-8-hydroxy-7,9-dioxo-N-(2,4,6-trifluorobenzyl)-2,3,4,5,7,9,13,13a-octahydro-2,5-methanopyrido[1',2':4,5]pyrazino[2,1-b][1,3]oxazepine-10-carboxamide; 8GB79LOJ07; (1S,11R,13R)-5-hydroxy-3,6-dioxo-N-[(2,4,6-trifluorophenyl)methyl]-12-oxa-2,9-diazatetracyclo[11.2.1.02,11.04,9]hexadeca-4,7-diene-7-carboxamide; Bictegravir [INN]; Bictegravir [USAN:INN]; bictegravirum; GS 9883; Bictegravir (USAN/INN); CHEMBL3989866; SCHEMBL15914278; GTPL11575; CHEBI:172943; BDBM330048; AMY12383; BCP25703; EX-A3161; GS9883; s5911; DB11799; DT-0020; 2,5-Methanopyrido(1',2':4,5)pyrazino(2,1-b)(1,3)oxazepine-10-carboxamide, 2,3,4,5,7,9,13,13a-octahydro-8-hydroxy-7,9-dioxo-N-((2,4,6-trifluorophenyl)methyl)-, (2R,5S,13aR)-; AC-30658; HY-17605; CS-0014685; D10909; N16998; US9663528, 42; A902376; Q27270406; GS-9883; GS 9883; GS9883; GS-9883-01; (1S,11R,13R)-5-hydroxy-3,6-dioxo-N-[(2,4,6-trifluorophenyl)methyl]-12-oxa-2,9-diazatetracyclo[11.2.1.0(2),(1)(1).0 , ]hexadeca-4,7-diene-7-carboxamide; (2R,5S,13aR)-8-hydroxy-7,9-dioxo-N-(2,4,6-trifluorobenzyl)-2,3,4,5,7,9,13,13a-octahydro-2,5-methanopyrido[1',2':4,5]pyrazino[2, 1-b][1,3]oxazepine-10-carboxamide
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
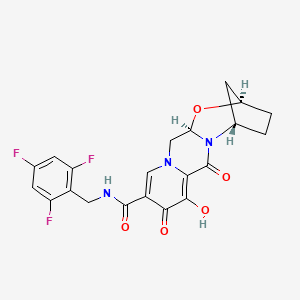
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[2]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[3]
|
||||
| Target | Human immunodeficiency virus Integrase (HIV IN) | POL_HV1B1 | [1] | ||
| Human immunodeficiency virus Reverse transcriptase (HIV RT) | POL_HV1B1 | [1] | |||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C21H18F3N3O5
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C1C[C@@H]2C[C@H]1N3[C@H](O2)CN4C=C(C(=O)C(=C4C3=O)O)C(=O)NCC5=C(C=C(C=C5F)F)F
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C21H18F3N3O5/c22-9-3-14(23)12(15(24)4-9)6-25-20(30)13-7-26-8-16-27(10-1-2-11(5-10)32-16)21(31)17(26)19(29)18(13)28/h3-4,7,10-11,16,29H,1-2,5-6,8H2,(H,25,30)/t10-,11+,16+/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
SOLUWJRYJLAZCX-LYOVBCGYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.G140S+p.Q148K+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.585 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
10
|
E
D
E
E
H
H
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
20
|
R
R
A
A
M
M
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
30
|
P
P
V
V
V
V
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
40
|
C
C
D
D
K
K
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
50
|
M
M
H
H
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
60
|
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
70
|
G
G
K
K
I
V
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
80
|
A
A
S
S
G
G
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
90
|
P
P
A
A
E
E
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
100
|
F
F
L
L
L
L
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
110
|
V
V
K
K
T
T
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
120
|
N
N
F
F
T
T
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
130
|
C
C
W
W
W
W
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
140
|
G
S
I
I
P
P
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
K
G
G
150
|
V
V
V
V
E
E
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
160
|
K
K
I
I
I
I
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
170
|
E
E
H
H
L
L
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
180
|
V
V
F
F
I
I
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
190
|
G
G
I
I
G
G
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
200
|
I
I
V
V
D
D
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
210
|
T
T
K
K
E
E
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
220
|
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
230
|
S
S
R
R
D
N
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
240
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
250
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
260
|
V
V
P
P
R
R
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
270
|
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
280
|
C
C
V
V
A
A
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E226Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D6T+p.K7E+p.S17N+p.V54I+p.I72V+p.L74M+p.V79I+p.T97A+p.L101I+p.I113L+p.S119R+p.T122I+p.T124N+p.T125A+p.E138K+p.G140A+p.I141AT+p.S147SG+p.Q148R+p.K156N+p.I203M+p.I208M+p.L234V+p.D253E |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 73.975 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
T
K
E
A
A
Q
Q
10
|
D
D
E
E
H
H
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
N
N
N
W
W
20
|
R
R
A
A
M
M
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
30
|
P
P
V
V
V
V
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
40
|
C
C
D
D
K
K
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
50
|
M
M
H
H
G
G
Q
Q
V
I
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
60
|
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
70
|
G
G
K
K
I
V
I
I
L
M
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
I
80
|
A
A
S
S
G
G
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
90
|
P
P
A
A
E
E
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
A
A
A
Y
Y
100
|
F
F
L
I
L
L
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
110
|
V
V
K
K
T
T
I
L
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
R
120
|
N
N
F
F
T
I
G
G
T
N
T
A
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
130
|
C
C
W
W
W
W
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
K
F
F
140
|
G
A
I
A
P
P
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
G
Q
R
G
G
150
|
V
V
V
V
E
E
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
N
E
E
L
L
K
K
160
|
K
K
I
I
I
I
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
170
|
E
E
H
H
L
L
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
180
|
V
V
F
F
I
I
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
190
|
G
G
I
I
G
G
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
200
|
I
I
V
V
D
D
I
M
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
M
Q
Q
210
|
T
T
K
K
E
E
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
220
|
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
230
|
S
S
R
R
N
N
P
P
L
V
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
240
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
250
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
D
E
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
260
|
V
V
P
P
R
R
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
270
|
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
280
|
C
C
V
V
A
A
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | TZM-bl cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B478 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Population sequencing of the integrase region assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, DTG, BIC, and CAB demonstrated a comparable activity on a panel of INSTI-resistant strains isolated from patients exposed to RAL, EVG, and/or DTG, with a significantly reduced susceptibility only with the pathway Q165H/k/R plus one to two additional INSTI mutations. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E11D+p.K14R+p.S17T+p.V31I+p.L45V+p.A91S+p.L101I+p.T124A+p.E138Q+p.G140C+p.Q148R+p.V151I+p.K219N+p.N222K+p.L234I+p.V259I |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.772 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
10
|
D
D
E
D
H
H
E
E
K
R
Y
Y
H
H
S
T
N
N
W
W
20
|
R
R
A
A
M
M
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
30
|
P
P
V
I
V
V
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
40
|
C
C
D
D
K
K
C
C
Q
Q
L
V
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
50
|
M
M
H
H
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
60
|
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
70
|
G
G
K
K
V
V
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
80
|
A
A
S
S
G
G
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
90
|
P
P
A
S
E
E
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
100
|
F
F
L
I
L
L
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
110
|
V
V
K
K
T
T
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
120
|
N
N
F
F
T
T
G
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
130
|
C
C
W
W
W
W
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
Q
F
F
140
|
G
C
I
I
P
P
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
R
G
G
150
|
V
V
V
I
E
E
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
160
|
K
K
I
I
I
I
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
170
|
E
E
H
H
L
L
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
180
|
V
V
F
F
I
I
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
190
|
G
G
I
I
G
G
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
200
|
I
I
V
V
D
D
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
210
|
T
T
K
K
E
E
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
N
220
|
I
I
Q
Q
N
K
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
230
|
S
S
R
R
N
N
P
P
L
I
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
240
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
250
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
I
260
|
V
V
P
P
R
R
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
270
|
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
280
|
C
C
V
V
A
A
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | TZM-bl cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B478 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Population sequencing of the integrase region assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, DTG, BIC, and CAB demonstrated a comparable activity on a panel of INSTI-resistant strains isolated from patients exposed to RAL, EVG, and/or DTG, with a significantly reduced susceptibility only with the pathway Q163H/k/R plus one to two additional INSTI mutations. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E11D+p.V31I+p.G70R+p.I84V+p.L101I+p.S119P+p.T122I+p.N155H+p.G163E+p.V201I+p.D256E |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.457 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
10
|
D
D
E
D
H
H
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
20
|
R
R
A
A
M
M
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
30
|
P
P
V
I
V
V
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
40
|
C
C
D
D
K
K
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
50
|
M
M
H
H
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
60
|
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
70
|
G
R
K
K
V
V
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
80
|
A
A
S
S
G
G
Y
Y
I
V
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
90
|
P
P
A
A
E
E
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
100
|
F
F
L
I
L
L
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
110
|
V
V
K
K
T
T
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
P
120
|
N
N
F
F
T
I
G
G
A
A
T
T
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
130
|
C
C
W
W
W
W
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
140
|
G
G
I
I
P
P
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
150
|
V
V
V
V
E
E
S
S
M
M
N
H
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
160
|
K
K
I
I
I
I
G
E
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
170
|
E
E
H
H
L
L
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
180
|
V
V
F
F
I
I
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
190
|
G
G
I
I
G
G
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
200
|
I
I
V
I
D
D
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
210
|
T
T
K
K
E
E
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
220
|
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
230
|
S
S
R
R
N
N
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
240
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
250
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
E
I
I
K
K
V
V
260
|
V
V
P
P
R
R
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
270
|
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
280
|
C
C
V
V
A
A
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | TZM-bl cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B478 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Population sequencing of the integrase region assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, DTG, BIC, and CAB demonstrated a comparable activity on a panel of INSTI-resistant strains isolated from patients exposed to RAL, EVG, and/or DTG, with a significantly reduced susceptibility only with the pathway Q161H/k/R plus one to two additional INSTI mutations. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K14R+p.S24G+p.D25E+p.S39C+p.I60IM+p.L63I+p.T97A+p.L101I+p.S119SR+p.T124N+p.T125A+p.I135V+p.E138T+p.G140S+p.Q148H+p.M154I+p.V165I+p.V201I+p.V259VI |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.011 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
R
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
G
D
E
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
C
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
M
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
I
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
V
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
A
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
I
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
R
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
T
N
T
A
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
V
K
K
Q
Q
E
T
F
F
G
S
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
H
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
I
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
I
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
I
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
I
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | TZM-bl cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B478 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Population sequencing of the integrase region assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, DTG, BIC, and CAB demonstrated a comparable activity on a panel of INSTI-resistant strains isolated from patients exposed to RAL, EVG, and/or DTG, with a significantly reduced susceptibility only with the pathway Q164H/k/R plus one to two additional INSTI mutations. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E11D+p.S17C+p.L68V+p.L101I+p.T124N+p.T125A+p.I135V+p.G140A+p.Q148R+p.D253E+p.V281M |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 73.975 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
D
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
C
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
V
E
E
G
G
K
K
V
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
I
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
T
N
T
A
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
V
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
A
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
R
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
E
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
M
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | TZM-bl cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B478 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Population sequencing of the integrase region assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, DTG, BIC, and CAB demonstrated a comparable activity on a panel of INSTI-resistant strains isolated from patients exposed to RAL, EVG, and/or DTG, with a significantly reduced susceptibility only with the pathway Q162H/k/R plus one to two additional INSTI mutations. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K14R+p.E69ED+p.E138K+p.G140S+p.Q148H+p.M154I+p.N155H+p.V201I |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.004 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
R
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
D
G
G
K
K
V
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
A
A
T
T
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
K
F
F
G
S
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
H
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
I
N
H
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
I
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | TZM-bl cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B478 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Population sequencing of the integrase region assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, DTG, BIC, and CAB demonstrated a comparable activity on a panel of INSTI-resistant strains isolated from patients exposed to RAL, EVG, and/or DTG, with a significantly reduced susceptibility only with the pathway Q166H/k/R plus one to two additional INSTI mutations. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S17N+p.M50L+p.I72V+p.Q95QH+p.T112V+p.I113V+p.T124A+p.T125A+p.G134D+p.V201I+p.Q221QKR+p.L234I+p.D256E |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.345 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
N
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
L
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
H
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
V
1260
|
I
V
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
T
A
T
A
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
D
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
I
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
K
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
I
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
E
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MT-2 cells | Umbilical cord blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2631 | |||||||||
| MT-4 cells | Umbilical cord blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2632 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR; DNA sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes in IN may contribute to bictegravir resistance or sensitivity. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K14R+p.V31I+p.I72V+p.T112V+p.I113V+p.T124A+p.T125A+p.G134N+p.I135V+p.D167E+p.V201I+p.T206S+p.I208L+p.N222K+p.L234I+p.A265V+p.R269K+p.S283G |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.188 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
R
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
I
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
V
1260
|
I
V
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
T
A
T
A
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
N
I
V
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
E
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
I
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
S
D
D
I
L
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
K
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
I
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
V
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
K
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
G
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MT-2 cells | Umbilical cord blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2631 | |||||||||
| MT-4 cells | Umbilical cord blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2632 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR; DNA sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes in IN may contribute to bictegravir resistance or sensitivity. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L101I+p.T122I+p.T124N+p.A265V |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.882 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
V
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
I
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
I
1270
|
G
G
T
N
T
T
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
V
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MT-2 cells | Umbilical cord blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2631 | |||||||||
| MT-4 cells | Umbilical cord blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2632 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR; DNA sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes in IN may contribute to bictegravir resistance or sensitivity. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S17N+p.L28I+p.P30A+p.I84L+p.S119T+p.T124A+p.K136Q+p.V165I+p.I200T+p.V201I+p.K211R+p.T218I+p.L234V+p.D256E+p.S283G |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.161 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
N
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
I
P
P
P
A
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
V
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
L
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
T
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
Q
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
I
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
T
V
I
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
R
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
I
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
V
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
E
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
G
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MT-2 cells | Umbilical cord blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2631 | |||||||||
| MT-4 cells | Umbilical cord blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2632 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR; DNA sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes in IN may contribute to bictegravir resistance or sensitivity. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E11D+p.D25E+p.V31I+p.F100Y+p.L101I+p.T112V+p.S119P+p.K136Q+p.V201I+p.T218I+p.L234I+p.A265V+p.R269K+p.D278A+p.S283G |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.612 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
D
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
E
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
I
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
V
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
Y
L
I
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
V
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
P
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
A
A
T
T
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
Q
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
I
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
I
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
I
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
V
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
K
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
A
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
G
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MT-2 cells | Umbilical cord blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2631 | |||||||||
| MT-4 cells | Umbilical cord blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2632 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR; DNA sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes in IN may contribute to bictegravir resistance or sensitivity. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G59D+p.I60V+p.E138K+p.Q148R+p.K173R+p.T218S+p.S230N+p.M275S+p.C280S |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | TZM-bl cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B478 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Population sequencing of the integrase region assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, DTG, BIC, and CAB demonstrated a comparable activity on a panel of INSTI-resistant strains isolated from patients exposed to RAL, EVG, and/or DTG, with a significantly reduced susceptibility only with the pathway Q160H/k/R plus one to two additional INSTI mutations. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T97A+p.G163R |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included T97A, G163R. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T122I |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included T122I. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.NULL |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included NULL. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.I72A+p.N155H |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included I72A, N155H. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E157K |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included E157K. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E92Q |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included E92Q. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S147G |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included S147G. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G140E |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included G140E. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.N155H |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included N155H. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L234F |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included L234F. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S24G+p.N155H+p.D253E |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included S24G, N155H, D253E. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E92Q+p.G140A |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included E92Q, G140A. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S153F |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included S153F. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T66I+p.R263K |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included T66I, R263K. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L45Q+p.T115H |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included L45Q, T115H. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R263K |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included R263K. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E138K+p.Q148R |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included E138K, Q148R. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S153Y |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included S153Y. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S153Y |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included S153Y. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q148R+p.N155H |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included Q148R, N155H. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T66I+p.Q148K |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included T66I, Q148K. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S153Y+p.L234F |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included S153Y, L234F. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G140A+p.Q148R |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included G140A, Q148R. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T97A+p.G118R |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included T97A, G118R. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G118R |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included G118R. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T66I+p.E138K+p.Q148R |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included T66I, E138K, Q148R. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E138K+p.Q148K |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included E138K, Q148K. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E138K+p.G140A+p.Q148R |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included E138K, G140A, Q148R. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T66I+p.E138K+p.Q148K |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included T66I, E138K, Q148K. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.G140S+p.Q148H+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 73.626 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
S
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
H
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E224Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.G140S+p.Q148R+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.84 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
S
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
R
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E223Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.N155H+p.E157Q+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.646 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
H
K
K
E
Q
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E221Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S119P+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.N155H+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.882 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
P
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
H
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E207Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.M50I+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.N155H+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.803 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
I
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
H
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E218Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.Q148R+p.E157Q+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.431 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
R
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
Q
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E193Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S119P+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.Q148R+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.614 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
P
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
R
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E200Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.M50I+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.Q148R+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.988 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
I
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
R
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E178Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.S147G+p.E157Q+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.081 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
G
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
Q
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E213Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S119P+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.S147G+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.949 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
P
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
G
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E199Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.M50I+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.S147G+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.838 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
I
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
G
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E192Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.E92Q+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.E157Q+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.844 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
Q
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
Q
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E212Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.E92Q+p.S119P+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.952 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
Q
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
P
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E217Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.M50I+p.I72V+p.E92Q+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.419 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
I
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
Q
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E204Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.T66I+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.E157Q+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.098 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
I
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
Q
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E162Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.T66I+p.I72V+p.S119P+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.357 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
I
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
P
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E161Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.M50I+p.T66I+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.344 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
I
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
I
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E160Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.E170A+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.934 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
A
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E191Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.G163K+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.915 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
K
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E190Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.E157Q+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.823 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
Q
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E206Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.E157K+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.67 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
K
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E216Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.S153Y+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.444 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
Y
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E220Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.S153F+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.101 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
F
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E219Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.S153A+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.227 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
A
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E198Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.V151L+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 73.653 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
L
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E189Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.V151A+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.213 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
A
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E177Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.Q146R+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.525 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
R
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E211Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.Q146P+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 73.737 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
P
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E159Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.Q146L+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.411 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
L
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E215Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.Q146K+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 69.778 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
K
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E188Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.Q146I+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 70.355 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
I
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E225Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.P145S+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.247 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
S
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E157Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.G140S+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.257 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
S
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E181Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.G140C+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.778 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
C
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E165Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.G140A+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.649 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
A
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E170Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.E138K+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.111 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
K
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E180Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.E138A+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.263 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
A
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E176Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.A128T+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.825 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
T
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E197Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.Q95R+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.746 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
R
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E196Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.Q95K+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.97 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
K
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E187Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72T+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.046 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
T
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E175Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72N+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.974 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
N
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E167Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72A+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.021 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
A
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E166Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.L68V+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.024 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
V
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E174Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.L68I+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.114 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
I
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E169Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.H51Y+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.596 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
Y
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E203Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.D232N+p.R263K |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.649 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
K
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E222Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.N155H+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.203 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
H
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E210Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.Q148R+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.686 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
R
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E173Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.Q148K+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.483 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
K
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E186Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.Q148H+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 73.704 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
H
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E172Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.S147G+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.607 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
G
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E195Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.Y143R+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 73.567 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
R
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E209Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.Y143H+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.08 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
H
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E185Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.Y143C+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 73.529 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
C
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E184Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.E92Q+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.029 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
Q
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E205Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.I72V+p.E92G+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 72.411 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
G
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E208Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.T66K+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.649 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
K
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E214Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.T66I+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.33 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
I
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E158Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.T66A+p.I72V+p.S123G+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.D232N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.085 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
A
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
S
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E164Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E10D+p.S17T+p.S39N+p.I72V+p.S119P+p.T122I+p.T124N+p.T125A+p.V151I+p.N155H+p.N222K+p.P261A |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.551 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
E
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
T
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
N
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
P
N
N
F
F
T
I
1270
|
G
G
T
N
T
A
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
I
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
H
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
K
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
A
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | TZM-bl cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B478 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Population sequencing of the integrase region assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, DTG, BIC, and CAB demonstrated a comparable activity on a panel of INSTI-resistant strains isolated from patients exposed to RAL, EVG, and/or DTG, with a significantly reduced susceptibility only with the pathway Q155H/k/R plus one to two additional INSTI mutations. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S17N+p.S39R+p.L45V+p.M50ML+p.T66A+p.V75I+p.L101I+p.T124A+p.K127R+p.S147SG+p.G163K+p.V201I |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.462 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
N
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
R
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
V
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
L
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
A
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
V
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
I
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
I
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
K
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
G
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
K
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
I
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | TZM-bl cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B478 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Population sequencing of the integrase region assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, DTG, BIC, and CAB demonstrated a comparable activity on a panel of INSTI-resistant strains isolated from patients exposed to RAL, EVG, and/or DTG, with a significantly reduced susceptibility only with the pathway Q148H/k/R plus one to two additional INSTI mutations. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A23T+p.S24G+p.D25E+p.L28I+p.I72V+p.T124A+p.Q148R+p.V165I+p.L172LF+p.H183HP+p.Q209QP+p.A239AT |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 73.352 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
T
S
G
D
E
F
F
N
N
L
I
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
R
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
I
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
F
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
P
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
P
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
T
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | TZM-bl cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B478 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Population sequencing of the integrase region assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, DTG, BIC, and CAB demonstrated a comparable activity on a panel of INSTI-resistant strains isolated from patients exposed to RAL, EVG, and/or DTG, with a significantly reduced susceptibility only with the pathway Q150H/k/R plus one to two additional INSTI mutations. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K7KR+p.S17N+p.I72V+p.I84L+p.T97A+p.L101I+p.T112I+p.S119P+p.T122I+p.T124N+p.T125A+p.K136Q+p.Y143R+p.V201I+p.A205S+p.K211R+p.T218L+p.L234V+p.D256E+p.I268L+p.D270H |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 73.893 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
R
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
N
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
L
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
A
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
I
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
I
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
P
N
N
F
F
T
I
1270
|
G
G
T
N
T
A
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
Q
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
R
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
I
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
S
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
R
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
L
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
V
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
E
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
L
R
R
D
H
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | TZM-bl cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B478 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Population sequencing of the integrase region assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, DTG, BIC, and CAB demonstrated a comparable activity on a panel of INSTI-resistant strains isolated from patients exposed to RAL, EVG, and/or DTG, with a significantly reduced susceptibility only with the pathway Q157H/k/R plus one to two additional INSTI mutations. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S17N+p.M154L+p.N155H+p.V201I+p.D232N+p.L242LF |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 73.66 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
N
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
V
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
A
A
T
T
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
L
N
H
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
I
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
D
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
F
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | TZM-bl cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B478 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Population sequencing of the integrase region assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, DTG, BIC, and CAB demonstrated a comparable activity on a panel of INSTI-resistant strains isolated from patients exposed to RAL, EVG, and/or DTG, with a significantly reduced susceptibility only with the pathway Q154H/k/R plus one to two additional INSTI mutations. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K14R+p.V31I+p.V32I+p.L45Q+p.L101I+p.T112V+p.T125A+p.G134N+p.I135V+p.K136T+p.Y143C+p.V201I+p.T206S+p.S230R+p.L234I+p.N254NS+p.R269K+p.D270H |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 73.008 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
R
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
I
V
I
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
Q
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
V
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
I
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
V
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
A
A
T
A
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
N
I
V
K
T
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
C
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
I
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
S
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
R
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
I
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
S
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
K
D
H
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | TZM-bl cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B478 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Population sequencing of the integrase region assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, DTG, BIC, and CAB demonstrated a comparable activity on a panel of INSTI-resistant strains isolated from patients exposed to RAL, EVG, and/or DTG, with a significantly reduced susceptibility only with the pathway Q158H/k/R plus one to two additional INSTI mutations. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K14R+p.S24H+p.V31I+p.L68I+p.I73V+p.E92Q+p.L101I+p.T112V+p.S119T+p.T124G+p.T125A+p.G134N+p.K136T+p.V165I+p.V201I+p.T206S+p.L234I+p.D256E+p.S283G |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 73.995 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
R
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
H
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
I
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
I
E
E
G
G
K
K
V
V
1220
|
I
V
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
Q
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
I
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
V
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
T
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
T
G
T
A
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
N
I
I
K
T
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
I
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
I
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
S
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
I
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
E
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
G
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | TZM-bl cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B478 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Population sequencing of the integrase region assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, DTG, BIC, and CAB demonstrated a comparable activity on a panel of INSTI-resistant strains isolated from patients exposed to RAL, EVG, and/or DTG, with a significantly reduced susceptibility only with the pathway Q149H/k/R plus one to two additional INSTI mutations. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K14R+p.V31I+p.T97A+p.L101I+p.T112V+p.S119R+p.T124A+p.T125S+p.G134N+p.K136T+p.N155H+p.V165I+p.V201I+p.T206S+p.Y227F+p.L234I+p.S255N+p.D256E+p.S283G |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.006 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
R
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
I
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
V
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
A
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
I
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
V
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
R
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
T
A
T
S
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
N
I
I
K
T
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
H
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
I
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
I
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
S
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
F
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
I
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
N
D
E
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
G
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | TZM-bl cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B478 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Population sequencing of the integrase region assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, DTG, BIC, and CAB demonstrated a comparable activity on a panel of INSTI-resistant strains isolated from patients exposed to RAL, EVG, and/or DTG, with a significantly reduced susceptibility only with the pathway Q153H/k/R plus one to two additional INSTI mutations. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S17N+p.R20K+p.M50I+p.V77A+p.L101I+p.T112I+p.T124A+p.T125A+p.K136Q+p.G193E+p.V201I+p.T206S+p.T218L+p.I220V+p.L234V+p.D256E+p.R263K+p.D279G+p.S283G |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.488 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
N
N
N
W
W
R
K
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
I
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
V
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
A
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
I
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
I
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
T
A
T
A
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
Q
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
I
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
S
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
L
K
K
I
V
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
V
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
E
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
K
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
G
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
G
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | TZM-bl cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B478 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Population sequencing of the integrase region assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, DTG, BIC, and CAB demonstrated a comparable activity on a panel of INSTI-resistant strains isolated from patients exposed to RAL, EVG, and/or DTG, with a significantly reduced susceptibility only with the pathway Q151H/k/R plus one to two additional INSTI mutations. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E11D+p.R20K+p.E92Q+p.V201I+p.K211R+p.S230SN+p.D232E+p.D256E |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.87 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
D
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
K
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
V
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
Q
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
A
A
T
T
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
I
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
R
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
N
R
R
D
E
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
E
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | TZM-bl cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B478 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Population sequencing of the integrase region assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, DTG, BIC, and CAB demonstrated a comparable activity on a panel of INSTI-resistant strains isolated from patients exposed to RAL, EVG, and/or DTG, with a significantly reduced susceptibility only with the pathway Q152H/k/R plus one to two additional INSTI mutations. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K14R+p.L101V+p.T112I+p.T125V+p.N155H+p.E157Q+p.K160Q+p.G193E+p.S230N+p.L234I+p.A265V+p.D279G |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 72.839 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
R
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
V
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
V
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
I
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
A
A
T
V
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
H
K
K
E
Q
L
L
K
K
K
Q
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
N
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
I
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
V
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
G
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | TZM-bl cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B478 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Population sequencing of the integrase region assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, DTG, BIC, and CAB demonstrated a comparable activity on a panel of INSTI-resistant strains isolated from patients exposed to RAL, EVG, and/or DTG, with a significantly reduced susceptibility only with the pathway Q156H/k/R plus one to two additional INSTI mutations. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S17N+p.D25E+p.S119G+p.T122I+p.T124N+p.T125A+p.M154I+p.N155H+p.K156R+p.T206S+p.T218S |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.293 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
N
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
E
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
V
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
G
N
N
F
F
T
I
1270
|
G
G
T
N
T
A
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
I
N
H
K
R
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
S
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
S
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | TZM-bl cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B478 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Population sequencing of the integrase region assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, DTG, BIC, and CAB demonstrated a comparable activity on a panel of INSTI-resistant strains isolated from patients exposed to RAL, EVG, and/or DTG, with a significantly reduced susceptibility only with the pathway Q159H/k/R plus one to two additional INSTI mutations. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.I5V+p.S17N+p.M50L+p.E69G+p.I72V+p.T112I+p.I113V+p.T124A+p.T125A+p.T174A+p.V201I+p.T218I+p.L234I+p.D256E |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.695 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
V
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
N
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
L
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
G
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
I
1260
|
I
V
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
T
A
T
A
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
A
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
I
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
I
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
I
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
E
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MT-2 cells | Umbilical cord blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2631 | |||||||||
| MT-4 cells | Umbilical cord blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2632 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR; DNA sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes in IN may contribute to bictegravir resistance or sensitivity. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K42Q+p.L101I+p.T112V+p.T124A+p.T125A+p.K136Q+p.G163R+p.V201I+p.L234I+p.R269K+p.D278A+p.S283G |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.483 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
Q
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
V
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
I
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
V
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
T
A
T
A
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
Q
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
R
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
I
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
I
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
K
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
A
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
G
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MT-2 cells | Umbilical cord blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2631 | |||||||||
| MT-4 cells | Umbilical cord blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2632 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR; DNA sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes in IN may contribute to bictegravir resistance or sensitivity. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K14R+p.V31I+p.L74I+p.L101I+p.T112V+p.T124A+p.T125A+p.G134N+p.I135V+p.K136T+p.H171Q+p.V201I+p.T206S+p.I208M+p.T218I+p.L234I+p.A265V+p.R269K+p.D286N |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 71.341 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
R
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
I
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
V
V
1220
|
I
I
L
I
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
I
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
V
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
T
A
T
A
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
N
I
V
K
T
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
Q
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
I
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
S
D
D
I
M
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
I
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
I
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
V
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
K
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
N
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MT-2 cells | Umbilical cord blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2631 | |||||||||
| MT-4 cells | Umbilical cord blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2632 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR; DNA sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes in IN may contribute to bictegravir resistance or sensitivity. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S17N+p.I72V+p.I84V+p.T124A+p.M154I+p.K173R |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.501 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
N
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
V
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
T
A
T
T
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
I
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
R
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MT-2 cells | Umbilical cord blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2631 | |||||||||
| MT-4 cells | Umbilical cord blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2632 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR; DNA sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes in IN may contribute to bictegravir resistance or sensitivity. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L101I+p.T125A+p.I135V+p.D167DE+p.G193R+p.V201I+p.I208L+p.K211T+p.A265V+p.S283G |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.45 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
V
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
I
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
A
A
T
A
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
V
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
E
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
R
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
I
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
L
Q
Q
T
T
K
T
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
V
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
G
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MT-2 cells | Umbilical cord blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2631 | |||||||||
| MT-4 cells | Umbilical cord blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2632 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR; DNA sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes in IN may contribute to bictegravir resistance or sensitivity. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K14R+p.A21T+p.A23V+p.S39N+p.I72V+p.T112V+p.T124A+p.T125A+p.G134N+p.I135V+p.K136R+p.D167E+p.V201I+p.L234I+p.S283G |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.133 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
R
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
T
M
M
1170
|
A
V
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
N
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
V
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
T
A
T
A
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
N
I
V
K
R
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
E
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
I
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
I
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
G
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MT-2 cells | Umbilical cord blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2631 | |||||||||
| MT-4 cells | Umbilical cord blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2632 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR; DNA sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes in IN may contribute to bictegravir resistance or sensitivity. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K14R+p.A21T+p.V31I+p.V32I+p.M50I+p.I72V+p.T112V+p.T124A+p.T125A+p.G134N+p.I135V+p.K136R+p.D167E+p.V201I+p.T206S+p.L234I+p.S283G |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.783 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
R
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
T
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
I
V
I
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
I
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
I
V
1220
|
I
I
L
L
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
V
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
T
A
T
A
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
N
I
V
K
R
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
E
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
I
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
S
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
I
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
G
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MT-2 cells | Umbilical cord blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2631 | |||||||||
| MT-4 cells | Umbilical cord blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2632 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR; DNA sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes in IN may contribute to bictegravir resistance or sensitivity. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L74M+p.T97A+p.S119G |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 73.492 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
V
V
1220
|
I
I
L
M
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
A
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
G
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
A
A
T
T
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included L74M, T97A, S119G. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L74M+p.T97A |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 73.068 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
V
V
1220
|
I
I
L
M
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
A
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
A
A
T
T
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included L74M, T97A. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L74M+p.T97A |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 73.068 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
V
V
1220
|
I
I
L
M
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
A
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
S
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
A
A
T
T
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included L74M, T97A. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L74M+p.T97A+p.S119T |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.127 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
V
V
1220
|
I
I
L
M
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
A
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
T
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
A
A
T
T
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included L74M, T97A, S119T. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L74M+p.T97A+p.S119P |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 73.599 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
V
V
1220
|
I
I
L
M
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
A
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
P
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
A
A
T
T
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included L74M, T97A, S119P. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L74M+p.T97A+p.S119R |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.412 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
V
V
1220
|
I
I
L
M
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
A
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
R
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
A
A
T
T
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included L74M, T97A, S119R. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L74M+p.T97A+p.S119R |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.412 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
V
V
1220
|
I
I
L
M
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
A
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
R
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
A
A
T
T
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included L74M, T97A, S119R. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L74M+p.S119P |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.456 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
V
V
1220
|
I
I
L
M
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
P
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
A
A
T
T
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included L74M, S119P. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L74M+p.S119R |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.816 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
V
V
1220
|
I
I
L
M
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
R
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
A
A
T
T
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included L74M, S119R. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L74M+p.S119R |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 75.736 |

|
||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: AlphaFold | Average pLDDT: 74.816 |

|
||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
F
F
L
L
1150
|
D
D
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
H
H
1160
|
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
H
H
S
S
N
N
W
W
R
R
A
A
M
M
1170
|
A
A
S
S
D
D
F
F
N
N
L
L
P
P
P
P
V
V
V
V
1180
|
A
A
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
A
A
S
S
C
C
D
D
K
K
1190
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
G
G
E
E
A
A
M
M
H
H
G
G
1200
|
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
C
C
S
S
P
P
G
G
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
1210
|
L
L
D
D
C
C
T
T
H
H
L
L
E
E
G
G
K
K
V
V
1220
|
I
I
L
M
V
V
A
A
V
V
H
H
V
V
A
A
S
S
G
G
1230
|
Y
Y
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
V
V
I
I
P
P
A
A
E
E
1240
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
A
A
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
1250
|
K
K
L
L
A
A
G
G
R
R
W
W
P
P
V
V
K
K
T
T
1260
|
I
I
H
H
T
T
D
D
N
N
G
G
S
R
N
N
F
F
T
T
1270
|
G
G
A
A
T
T
V
V
R
R
A
A
A
A
C
C
W
W
W
W
1280
|
A
A
G
G
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
I
I
P
P
1290
|
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
E
E
1300
|
S
S
M
M
N
N
K
K
E
E
L
L
K
K
K
K
I
I
I
I
1310
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
H
H
L
L
1320
|
K
K
T
T
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
F
F
I
I
1330
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
K
K
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
I
I
G
G
1340
|
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
G
G
E
E
R
R
I
I
V
V
D
D
1350
|
I
I
I
I
A
A
T
T
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
K
K
E
E
1360
|
L
L
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
K
K
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
1370
|
F
F
R
R
V
V
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
S
S
R
R
N
N
1380
|
P
P
L
L
W
W
K
K
G
G
P
P
A
A
K
K
L
L
L
L
1390
|
W
W
K
K
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
V
V
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
1400
|
D
D
N
N
S
S
D
D
I
I
K
K
V
V
V
V
P
P
R
R
1410
|
R
R
K
K
A
A
K
K
I
I
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
1420
|
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
G
G
D
D
D
D
C
C
V
V
A
A
1430
|
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
D
D
E
E
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included L74M, S119R. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G163R |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E202Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F121Y |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E163Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S119T |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E183Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S119R |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E201Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S119P |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E182Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S119G |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E179Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L74M |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E171Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.M50I |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E194Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T97A |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IN sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Total 6 of 39 minor INSTI-R mutations (M50I, S119P/G/T/R, and E157Q) were found in >1% of IN-treatment-na ve subjects with no impact on INSTI susceptibility. When each combined with major INSTI-R mutation, M50I, S119P, and E168Q led to decreased susceptibility to elvitegravir but remained sensitive to dolutegravir and bictegravir. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V88I+p.M154I |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MT-2 cells | Umbilical cord blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2631 | |||||||||
| MT-4 cells | Umbilical cord blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2632 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR; DNA sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes in IN may contribute to bictegravir resistance or sensitivity. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T97A+p.S119G |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included T97A, S119G. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T97A+p.S119T |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included T97A, S119T. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T97V |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included T97V. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L74M |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included L74M. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T66I |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included T66I. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T97A+p.G118R+p.S119R |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included T97A, G118R, S119R. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L74M |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included L74M. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T97A+p.S119P |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included T97A, S119P. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Integrase (HIV1 IT) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T97A |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; GeneSeq assay; Population sequencing of the integrase region assay; DNA sequencing assay; Site-directed mutagenesis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
PhenoSense assay; Viral load assay; A single-cycle assay; TZM-bl cell line-based phenotypic assay; SDMs and phenotyping assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some mutations identified were assiacted with resistance in the HIV isolates, those mutations included T97A. | ||||||||||||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
