Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00291) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Coumermycin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
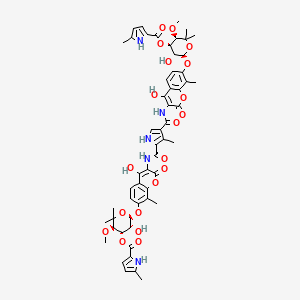
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(2 diseases)
[2]
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Bacterial DNA gyrase B (Bact gyrB) | GYRB_ECOLI | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C55H59N5O20
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC1=CC=C(N1)C(=O)O[C@H]2[C@H]([C@@H](OC([C@@H]2OC)(C)C)OC3=C(C4=C(C=C3)C(=C(C(=O)O4)NC(=O)C5=CNC(=C5C)C(=O)NC6=C(C7=C(C(=C(C=C7)O[C@H]8[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H](C(O8)(C)C)OC)OC(=O)C9=CC=C(N9)C)O)C)OC6=O)O)O)C)O
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C55H59N5O20/c1-21-12-16-29(57-21)48(67)77-42-38(63)52(79-54(6,7)44(42)71-10)73-31-18-14-26-36(61)34(50(69)75-40(26)24(31)4)59-46(65)28-20-56-33(23(28)3)47(66)60-35-37(62)27-15-19-32(25(5)41(27)76-51(35)70)74-53-39(64)43(45(72-11)55(8,9)80-53)78-49(68)30-17-13-22(2)58-30/h12-20,38-39,42-45,52-53,56-58,61-64H,1-11H3,(H,59,65)(H,60,66)/t38-,39-,42+,43+,44-,45-,52-,53-/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
WTIJXIZOODAMJT-DHFGXMAYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: DNA gyrase subunit B (GYRB) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R136C+p.R136H+p.R136S+p.G164V |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli HB101 | 634468 | ||
| Escherichia coli JM109 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain N4177 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain CC1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain CC5 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain LE234 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain LE316 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Coumarins are inhibitors of the ATP hydrolysis and DNA supercoiling reactions catalysed by DNA gyrase. four mutations have been identified regaeding conferring coumarin resistance to Escherichia coli: Arg-136 to Cys, His or Ser and Gly-164 to Val.Significant differences in the susceptibility of mutant GyrB proteins to inhibition by either chlorobiocin and novobiocin or coumermycin have been found, suggesting wider contacts between coumermycin and GyrB. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: DNA topoisomerase 4 subunit B (PARE) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bartonella bacilliformis infection [ICD-11: 1C11.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G124S |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli HB101 | 634468 | ||
| Bartonella bacilliformis kC583 | 360095 | |||
| Bartonella bacilliformis strain CR1-CR12 | 774 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain N4177 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain N99 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain TOP10F' | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA hybridizations assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | First, in 5 of the 12 coumermycin A1-resistant strains (CR1, CR2, CR6, CR8, and CR9), identical G-to-A transitions at base 370 of the 2,079-bp ORF resulted in a deduced Gly124-to-Ser (Gly124-Ser) substitution. Second, 4 of the 12 resistant strains (CR4, CR7, CR11, and CR12) carried a G-to-A transition at base 550 that resulted in a deduced Arg184-Gln substitution. The third loci at which lesions were detected occurred in the Thr214 codon, in which two different transitions were observed with two distinct deduced substitutions; the ACA-to-GCA transition resulted in a Thr214-Ala substitution (CR3), whereas the ACA-to-ATA transition resulted in a Thr214-Ile substitution (CR5, CR10). The MICs for GyrB mutants represented by strains CR3, CR4, and CR9 were determined to be 0.2 ug/ml, whereas the MIC for CR5 was 0.3 ug/ml. This suggests that a Thr214-Ile substitution confers a higher level of resistance than Thr214-Ala, Gly124-Ser, or Arg184-Gln, consistent with findings in B. burgdorferi. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA topoisomerase 4 subunit B (PARE) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bartonella bacilliformis infection [ICD-11: 1C11.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R184Q |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli HB101 | 634468 | ||
| Bartonella bacilliformis kC583 | 360095 | |||
| Bartonella bacilliformis strain CR1-CR12 | 774 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain N4177 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain N99 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain TOP10F' | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA hybridizations assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | First, in 5 of the 12 coumermycin A1-resistant strains (CR1, CR2, CR6, CR8, and CR9), identical G-to-A transitions at base 370 of the 2,079-bp ORF resulted in a deduced Gly124-to-Ser (Gly124-Ser) substitution. Second, 4 of the 12 resistant strains (CR4, CR7, CR11, and CR12) carried a G-to-A transition at base 550 that resulted in a deduced Arg184-Gln substitution. The third loci at which lesions were detected occurred in the Thr214 codon, in which two different transitions were observed with two distinct deduced substitutions; the ACA-to-GCA transition resulted in a Thr214-Ala substitution (CR3), whereas the ACA-to-ATA transition resulted in a Thr214-Ile substitution (CR5, CR10). The MICs for GyrB mutants represented by strains CR3, CR4, and CR9 were determined to be 0.2 ug/ml, whereas the MIC for CR5 was 0.3 ug/ml. This suggests that a Thr214-Ile substitution confers a higher level of resistance than Thr214-Ala, Gly124-Ser, or Arg184-Gln, consistent with findings in B. burgdorferi. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA topoisomerase 4 subunit B (PARE) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bartonella bacilliformis infection [ICD-11: 1C11.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y214A |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli HB101 | 634468 | ||
| Bartonella bacilliformis kC583 | 360095 | |||
| Bartonella bacilliformis strain CR1-CR12 | 774 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain N4177 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain N99 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain TOP10F' | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA hybridizations assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | First, in 5 of the 12 coumermycin A1-resistant strains (CR1, CR2, CR6, CR8, and CR9), identical G-to-A transitions at base 370 of the 2,079-bp ORF resulted in a deduced Gly124-to-Ser (Gly124-Ser) substitution. Second, 4 of the 12 resistant strains (CR4, CR7, CR11, and CR12) carried a G-to-A transition at base 550 that resulted in a deduced Arg184-Gln substitution. The third loci at which lesions were detected occurred in the Thr214 codon, in which two different transitions were observed with two distinct deduced substitutions; the ACA-to-GCA transition resulted in a Thr214-Ala substitution (CR3), whereas the ACA-to-ATA transition resulted in a Thr214-Ile substitution (CR5, CR10). The MICs for GyrB mutants represented by strains CR3, CR4, and CR9 were determined to be 0.2 ug/ml, whereas the MIC for CR5 was 0.3 ug/ml. This suggests that a Thr214-Ile substitution confers a higher level of resistance than Thr214-Ala, Gly124-Ser, or Arg184-Gln, consistent with findings in B. burgdorferi. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA topoisomerase 4 subunit B (PARE) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bartonella bacilliformis infection [ICD-11: 1C11.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y214I |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli HB101 | 634468 | ||
| Bartonella bacilliformis kC583 | 360095 | |||
| Bartonella bacilliformis strain CR1-CR12 | 774 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain N4177 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain N99 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain TOP10F' | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA hybridizations assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | First, in 5 of the 12 coumermycin A1-resistant strains (CR1, CR2, CR6, CR8, and CR9), identical G-to-A transitions at base 370 of the 2,079-bp ORF resulted in a deduced Gly124-to-Ser (Gly124-Ser) substitution. Second, 4 of the 12 resistant strains (CR4, CR7, CR11, and CR12) carried a G-to-A transition at base 550 that resulted in a deduced Arg184-Gln substitution. The third loci at which lesions were detected occurred in the Thr214 codon, in which two different transitions were observed with two distinct deduced substitutions; the ACA-to-GCA transition resulted in a Thr214-Ala substitution (CR3), whereas the ACA-to-ATA transition resulted in a Thr214-Ile substitution (CR5, CR10). The MICs for GyrB mutants represented by strains CR3, CR4, and CR9 were determined to be 0.2 ug/ml, whereas the MIC for CR5 was 0.3 ug/ml. This suggests that a Thr214-Ile substitution confers a higher level of resistance than Thr214-Ala, Gly124-Ser, or Arg184-Gln, consistent with findings in B. burgdorferi. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
