Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00220) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Oxacillin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Bactocill; Ossacillina; Oxacilina; Oxacilline; Oxacillinum; Oxazocillin; Oxazocilline; Prostaphlin; Prostaphlyn; OXACILLIN SODIUM; Ossacillina [DCIT]; Sodium oxacillin; Bactocill (TN); MPI-penicillin; MPi-PC; Oxacilina (TN); Oxacilina [INN-Spanish]; Oxacillin (INN); Oxacillin [INN:BAN]; Oxacilline [INN-French]; Oxacillinum [INN-Latin]; Penicillin, Methylphenylisoxazolyl; Oxacillin, Monosodium Salt, Anhydrous; (2S,5R,6R)-3,3-dimethyl-6-[(5-methyl-3-phenyl-1,2-oxazole-4-carbonyl)amino]-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid; (2S,5R,6R)-3,3-dimethyl-6-{[(5-methyl-3-phenylisoxazol-4-yl)carbonyl]amino}-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid; (5-methyl-3-phenyl-4-isoxazolyl)penicillin; 2,2-dimethyl-6beta-(5-methyl-3-phenyl-1,2-oxazole-4-carboxamido)penam-3alpha-carboxylic acid; 5-Methyl-3-phenyl-4-isoxazolyl-penicillin; 6beta-(5-methyl-3-phenylisoxazol-4-yl)penicillanic acid
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
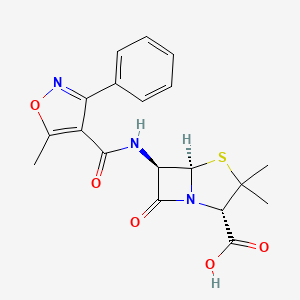
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[3]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(2 diseases)
[4]
[5]
|
||||
| Target | Bacterial Penicillin binding protein (Bact PBP) | NOUNIPROTAC | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C19H19N3O5S
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC1=C(C(=NO1)C2=CC=CC=C2)C(=O)N[C@H]3[C@@H]4N(C3=O)[C@H](C(S4)(C)C)C(=O)O
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C19H19N3O5S/c1-9-11(12(21-27-9)10-7-5-4-6-8-10)15(23)20-13-16(24)22-14(18(25)26)19(2,3)28-17(13)22/h4-8,13-14,17H,1-3H3,(H,20,23)(H,25,26)/t13-,14+,17-/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
UWYHMGVUTGAWSP-JKIFEVAISA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [1], [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv | 83332 | ||
| Escherichia coli DH10B | 316385 | |||
| Mycobacterium smegmatis PM274 | 1772 | |||
| Mycobacterium smegmatis PM759 | 1772 | |||
| Mycobacterium smegmatis PM791 | 1772 | |||
| Mycobacterium smegmatis PM876 | 1772 | |||
| Mycobacterium smegmatis PM939 | 1772 | |||
| Mycobacterium smegmatis PM976 | 1772 | |||
| Mycobacterium tuberculosis PM638 | 1773 | |||
| Mycobacterium tuberculosis PM669 | 1773 | |||
| Mycobacterium tuberculosis PM670 | 1773 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion test assay; E-strip test assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mycobacteria produce Beta-lactamases and are intrinsically resistant to Beta-lactam antibiotics.The mutants M. tuberculosis PM638 (detablaC1) and M. smegmatis PM759 (detablaS1) showed an increase in susceptibility to Beta-lactam antibiotics. | |||
| Key Molecule: Penicillin binding protein PBP 2 (PBP2) | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus RN4220 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus M10/0061 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus M10/0148 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus WGB8404 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion test assay; Etest assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Methicillin resistance in staphylococci is mediated by penicillin binding protein 2a (PBP 2a), encoded by mecA on mobile staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) elements.Whole-genome sequencing of one isolate (M10/0061) revealed a 30-kb SCCmec element encoding a class E mec complex with highly divergent blaZ-mecA-mecR1-mecI, a type 8 cassette chromosome recombinase (ccr) complex consisting of ccrA1-ccrB3, an arsenic resistance operon, and flanking direct repeats (DRs). | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Tetracycline resistance protein class A (TETA) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Corynebacterium striatum infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Corynebacterium glutamicum strain ATCC 13032 | 196627 | ||
| Corynebacterium striatum strain M82B | 43770 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain DH5alphaMCR | 668369 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Macrodilution broth method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The large multiresistance plasmid pTP10 was initially identified in the clinical isolate C. striatum M82B. This 51-kb R-plasmid was shown to carry the determinants for resistance to the antibiotics chloramphenicol, erythomycin, kanamycin, and tetracycline by ethidium bromide-based curing experiments. The tetracycline and oxacillin resistance region is part of a DNA segment structurally similar to the chromosome of the human pathogen Mycobacterium tuberculosis. A resistance assay in C. glutamicum demonstrated that the tetAB gene pair of pTP10 is necessary to confer resistance to the antibiotics tetracycline and oxytetracycline. | |||
| Key Molecule: Tetracycline resistance protein class A (TETA) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Corynebacterium glutamicum infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Corynebacterium glutamicum strain ATCC 13032 | 196627 | ||
| Corynebacterium striatum strain M82B | 43770 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain DH5alphaMCR | 668369 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Macrodilution broth method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The large multiresistance plasmid pTP10 was initially identified in the clinical isolate C. striatum M82B. This 51-kb R-plasmid was shown to carry the determinants for resistance to the antibiotics chloramphenicol, erythomycin, kanamycin, and tetracycline by ethidium bromide-based curing experiments. Both resistance genes are located on mobile DNA elements that are capable of transposition into the chromosome of the non-pathogenic soil bacteriumC. glutamicum. A resistance assay in C. glutamicum demonstrated that the tetAB gene pair of pTP10 is necessary to confer resistance to the antibiotics tetracycline and oxytetracycline. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: P-type ATPase zinc transporter Rv3270 | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bone infection [ICD-11: 1B2Z.9] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | E. coli XL1-Blue | 562 | ||
| E. coli CS109 | 562 | |||
| M. smegmatis MC2 159 | 1772 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Gene expression analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Antimicrobial susceptibility assay; Intracellular drug accumulation activity assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Metal homeostasis is maintained by the uptake, storage and efflux of metal ions that are necessary for the survival of the bacterium. Homeostasis is mostly regulated by a group of transporters categorized as ABC transporters and P-type ATPases. On the other hand, efflux pumps often play a role in drug-metal cross-resistance. Here, with the help of antibiotic sensitivity, antibiotic/dye accumulation and semi-quantitative biofilm formation assessments we report the ability of Rv3270, a P-type ATPase known for its role in combating Mn2+ and Zn2+ metal ion toxicity in Mycobacterium tuberculosis, in influencing the extrusion of multiple structurally unrelated drugs and enhancing the biofilm formation of Escherichia coli and Mycobacterium smegmatis. Overexpression of Rv3270 increased the tolerance of host cells to norfloxacin, ofloxacin, sparfloxacin, ampicillin, oxacillin, amikacin and isoniazid. A significantly lower accumulation of norfloxacin, ethidium bromide, bocillin FL and levofloxacin in cells harbouring Rv3270 as compared to host cells indicated its role in enhancing efflux activity. Although over-expression of Rv3270 did not alter the susceptibility levels of levofloxacin, rifampicin and apramycin, the presence of a sub-inhibitory concentration of Zn2+ resulted in low-level tolerance towards these drugs. Of note, the expression of Rv3270 enhanced the biofilm-forming ability of the host cells strengthening its role in antimicrobial resistance. Therefore, the study indicated that the over-expression of Rv3270 enhances the drug efflux activity of the micro-organism where zinc might facilitate drug-metal cross-resistance for some antibiotics. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Membrane-associated protein TcaA (tcaA) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
E-test assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The MIC of penicillin plus clavulanate decreased from 3 mg/L to 0.064 mg/L and that of oxacillin decreased from 16 to 0.5 mg/L when?tcaA?was knocked out in the LAC strain. Compared with wild-type MRSA isolates, when?tcaA?was deleted, all selected strains were more susceptible to beta-lactams. Susceptibility to ceftobiprole was restored in the ceftobiprole-resistant strain when?tcaA?was deleted.?tcaA?knockout caused "log-like" abnormal division of MRSA, and?tcaA?deficiency mediated low expression of?mecA, ponA, and?murA2. tcaA is a potential resistance breaker target for beta-lactams, including ceftobiprole, in MRSA. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Membrane-associated protein TcaA (tcaA) | [5] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
E-test assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The MIC of penicillin plus clavulanate decreased from 3 mg/L to 0.064 mg/L and that of oxacillin decreased from 16 to 0.5 mg/L when?tcaA?was knocked out in the LAC strain. Compared with wild-type MRSA isolates, when?tcaA?was deleted, all selected strains were more susceptible to beta-lactams. Susceptibility to ceftobiprole was restored in the ceftobiprole-resistant strain when?tcaA?was deleted.?tcaA?knockout caused "log-like" abnormal division of MRSA, and?tcaA?deficiency mediated low expression of?mecA, ponA, and?murA2. tcaA is a potential resistance breaker target for beta-lactams, including ceftobiprole, in MRSA. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
