Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00191) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Mefloquine
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Lariam; Mefloquin; Mefloquina; Mefloquinone; Mefloquinum; Mephloquine; Racemic mefloquine; Ro 215998; WR 142490; Lariam (Hydrochloride); Lariam (TN); Mefaquin (TN); Mefloquina [INN-Spanish]; Mefloquinum [INN-Latin]; RO 13-7224; RO 13-7225; Ro 21-5998; SPB-80406; WR-142490; Mefloquine (USAN/INN); Mefloquine [USAN:INN:BAN]; RTI1169-1-1; RTI1172-1-1; RTI1173-1-1; RTI1174-1-1; RTI1188-1-1; RTI1189-1-1; Ro 21-5998 (Hydrochloride); WR-142,490; WR-177,602; Ro-21-5998-001; Alpha-2-Piperidinyl-2,8-bis(trifluoromethyl)-4-quinolinemethanol; Alpha-2-Piperidyl-2,8-bis(trifluoromethyl)quinoline-4-methanol; [2,8-bis(trifluoromethyl)quinolin-4-yl]-piperidin-2-ylmethanol; Erthro-.alpha.-[2-piperidyl]-2,8-bis[trifluoromethyl]-4-quinolinemethanol; (+)-(11R,2'S)-erythro-Mefloquine; (+)-Mefloquine; (+)-Threo-Mefloquine; (-)-(11S,2'R)-erythro-Mefloquine; (-)-Mefloquine; (-)-Threo-Mefloquine; (DL-erythro-alpha-2-Piperidyl-2,8-bis(trifluoromethyl)-4-quinolinemethanol; (R)-[2,8-bis(trifluoromethyl)quinolin-4-yl]-[(2R)-piperidin-2-yl]methanol; (R)-[2,8-bis(trifluoromethyl)quinolin-4-yl]-[(2S)-piperidin-2-yl]methanol; (S)-[2,8-bis(trifluoromethyl)quinolin-4-yl]-[(2R)-piperidin-2-yl]methanol; (S)-[2,8-bis(trifluoromethyl)quinolin-4-yl]-[(2S)-piperidin-2-yl]methanol; (S)-[2,8-bis(trifluoromethyl)quinolin-4-yl][(2R)-piperidin-2-yl]methanol
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
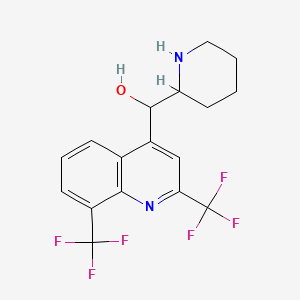
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(1 diseases)
|
||||
| Target | Plasmodium 80S ribosome (Malaria 80S) | NOUNIPROTAC | [2] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C17H16F6N2O
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C1CCNC(C1)C(C2=CC(=NC3=C2C=CC=C3C(F)(F)F)C(F)(F)F)O
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C17H16F6N2O/c18-16(19,20)11-5-3-4-9-10(15(26)12-6-1-2-7-24-12)8-13(17(21,22)23)25-14(9)11/h3-5,8,12,15,24,26H,1-2,6-7H2
|
||||
| InChIKey |
XEEQGYMUWCZPDN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Multidrug resistance protein 1 (ABCB1) | [1], [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Malaria [ICD-11: 1F45.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasmodium falciparum strains | 5833 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SYBR Green I detection assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Increasingly, molecular genetic markers for antimalarial drug resistance have been identified, an advance that facilitates the monitoring of the emergence and spread of resistance. Currently, reliable molecular markers are available for P. falciparum resistance to artemisinins (mutations in the propeller region of Pfkelch), sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine (mutations in the dihydrofolate reductase [PfDHFR] and dihydropteroate synthase [PfDHPS] genes), mefloquine (MQ) (amplification of the multidrug resistance-1 gene [PfMDR1]), and piperaquine (amplification of PfPlasmepsin2/3 and specific mutations in the P. falciparum chloroquine resistance transporter gene. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Chloroquine resistance transporter (CRT) | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Malaria [ICD-11: 1F45.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.N86Y |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasmodium falciparum strains | 5833 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
MIP probes and PCR sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SYBR Green I detection assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Despite the availability of few mutant parasites for comparison, the PfMDR1 Asn86Tyr substitution appeared to be associated with increased susceptibility to lumefantrine and mefloquine, as seen prev. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multidrug resistance protein 1 (ABCB1) | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Malaria [ICD-11: 1F45.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.N86+p.Y184 |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasmodium falciparum isolates | 5833 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Quantitative trait loci (QTL) assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SYBR Green I detection assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | By QTL analysis, lumefantrine and mefloquine phenotypes mapped to a chromosome 5 region containing codon polymorphisms N86Y and Y184F in the P. falciparum multidrug resistance 1 protein. | |||
| Key Molecule: Chloroquine resistance transporter (CRT) | [4] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Malaria [ICD-11: 1F45.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K76T |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasmodium falciparum strains | 5833 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Nested PCR | |||
| Mechanism Description | Both in vitro and molecular surveillance studies have associated CQ resistance mainly with the pfcrt 76T allele, but also with pfmdr1 86Y and 184F alleles. Pfcrt 76T and pfmdr1 86Y mutant alleles have also been reported to decrease P. falciparum susceptibility to amodiaquine but increase parasite sensitivity to dihydroartemisinin, lumefantrine and mefl. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multidrug resistance protein 1 (ABCB1) | [4] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Malaria [ICD-11: 1F45.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y184F |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasmodium falciparum strains | 5833 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Nested PCR | |||
| Mechanism Description | Both in vitro and molecular surveillance studies have associated CQ resistance mainly with the pfcrt 76T allele, but also with pfmdr1 86Y and 184F alleles. Pfcrt 76T and pfmdr1 86Y mutant alleles have also been reported to decrease P. falciparum susceptibility to amodiaquine but increase parasite sensitivity to dihydroartemisinin, lumefantrine and mefl. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
