Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00184) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Cephaloridine
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Cephaloridine; cefaloridine; Cefaloridin; Cephaloridin; Cephaloridinum; Cepaloridin; Cefalorizin; Cephalomycine; Cefaloridinum; Cepalorin; Cefaloridina; Loridine; Ceflorin; 50-59-9; Kefloridin; Glaxoridin; Ceporin; Vioviantine; Intrasporin; Sefacin; Keflordin; Deflorin; Cilifor; Ceporan; Sasperin; Faredina; Ceporine; Keflodin; Verolgin; Lloncefal; Kefspor; Ampligram; Betaine cephaloridine; CHEBI:3537; UNII-LVZ1VC61HB; Cefaloridinum [INN-Latin]; Cefaloridina [INN-Spanish]; N-(7-(2'-Thienylacetamidoceph-3-ylmethyl))-pyridinium-2-carboxylate; SCH
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
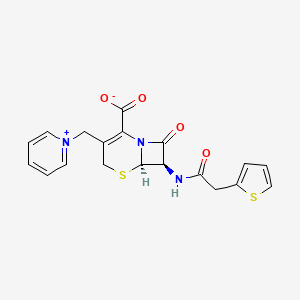
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(2 diseases)
[4]
[5]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(1 diseases)
|
||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C19H17N3O4S2
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C1C(=C(N2[C@H](S1)[C@@H](C2=O)NC(=O)CC3=CC=CS3)C(=O)[O-])C[N+]4=CC=CC=C4
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C19H17N3O4S2/c23-14(9-13-5-4-8-27-13)20-15-17(24)22-16(19(25)26)12(11-28-18(15)22)10-21-6-2-1-3-7-21/h1-8,15,18H,9-11H2,(H-,20,23,25,26)/t15-,18-/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
CZTQZXZIADLWOZ-CRAIPNDOSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 | 208964 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing and protein assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | P. aeruginosa harbors two naturally encoded Beta-lactamase genes, one of which encodes an inducible cephalosporinase and the other of which encodes a constitutively expressed oxacillinase. AmpC is a kind of cephalosporinase which lead to drug resistance. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Outer membrane porin C (OMPC) | [1], [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli 1422 | 562 | ||
| Escherichia coli 1437 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli B1343 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli B1350 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli B1421 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli pop1010 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion test assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Permeability of the outer membrane to lowmolecular-weight hydrophilic molecules is due to the presence of porin protein molecules such as OmpF and OmpC, which form pores in the outer membrane that allow small molecules to diffuse rapidly into the periplasmic space.The case of cephaloridine and cefazolin is remarkable because mutants lacking the OmpF or the OmpC proteins individually were as susceptible to cefaloridine and cefazolin as was the wild type, but mutants lacking both proteins were resistant to these Beta-lactams. | |||
ICD-12: Respiratory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Bcr/CflA family efflux transporter (BCML) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Klebsiella pneumoniae infection [ICD-11: CA40.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli DH10B | 316385 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain NCTC 50192 | 562 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strain ORI-1 | 573 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and hybridization experiments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution technique assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Klebsiella pneumoniae ORI-1 strain harbored a ca. 140-kb nontransferable plasmid, pTk1, that conferred an extended-spectrum cephalosporin resistance profile antagonized by the addition of clavulanic acid, tazobactam, or imipenem. The gene for GES-1 (Guiana extended-spectrum beta-lactamase) was cloned, and its protein was expressed in Escherichia coli DH10B, where this pI-5. 8 beta-lactamase of a ca. 31-kDa molecular mass conferred resistance to oxyimino cephalosporins (mostly to ceftazidime). GES-1 is weakly related to the other plasmid-located Ambler class A extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs). | |||
| Key Molecule: Bcr/CflA family efflux transporter (BCML) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Klebsiella pneumoniae infection [ICD-11: CA40.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli DH10B | 316385 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain NCTC 50192 | 562 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strain ORI-1 | 573 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and hybridization experiments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution technique assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Beta-Lactam MICs for k. pneumoniae ORI-1 and Escherichia coli DH10B harboring either the natural plasmid pTk1 or the recombinant plasmid pC1 were somewhat similar and might indicate the presence of an ESBL. In all cases, the ceftazidime MICs were higher than those of cefotaxime and aztreonam. Beta-Lactam MICs were always lowered by the addition of clavulanic acid or tazobactam, less so by sulbactam, and uncommonly by imipenem. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Bcr/CflA family efflux transporter (BCML) | [5] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Klebsiella pneumoniae infection [ICD-11: CA40.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Antagonism |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli DH10B | 316385 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain NCTC 50192 | 562 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strain ORI-1 | 573 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and hybridization experiments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution technique assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Inhibition studies, as measured by IC50 values with benzylpenicillin as the substrate, showed that GES-1 was inhibited by clavulanic acid (5 uM) and tazobactam (2.5 uM) and strongly inhibited by imipenem (0.1 uM). Beta-Lactam MICs were always lowered by the addition of clavulanic acid or tazobactam, less so by sulbactam, and uncommonly by imipenem. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
