Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00156) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Ceftobiprole
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
BAL 9141; BAL 9141-000; BAL-9141; Ro 63-9141; Ro-63-9141; Ro-63-9141/000; (6R,7R)-7-[[(2Z)-2-(5-amino-1,2,4-thiadiazol-3-ylidene)-2-nitrosoacetyl]amino]-8-oxo-3-[(E)-[2-oxo-1-[(3R)-pyrrolidin-3-yl]pyrrolidin-3-ylidene]methyl]-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 2 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
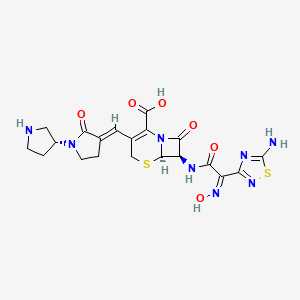
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(1 diseases)
|
||||
| Target | Bacterial Penicillin binding protein (Bact PBP) | NOUNIPROTAC | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C20H22N8O6S2
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C1CNC[C@@H]1N2CC/C(=C\\C3=C(N4[C@@H]([C@@H](C4=O)NC(=O)/C(=N\\O)/C5=NSC(=N5)N)SC3)C(=O)O)/C2=O
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C20H22N8O6S2/c21-20-24-14(26-36-20)11(25-34)15(29)23-12-17(31)28-13(19(32)33)9(7-35-18(12)28)5-8-2-4-27(16(8)30)10-1-3-22-6-10/h5,10,12,18,22,34H,1-4,6-7H2,(H,23,29)(H,32,33)(H2,21,24,26)/b8-5+,25-11-/t10-,12-,18-/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
VOAZJEPQLGBXGO-SDAWRPRTSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-12: Respiratory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Penicillin-binding protein 2X (PBP2X) | [1], [2], [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Community-acquired pneumonia [ICD-11: CA40.2] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.M339F |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.66 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.42 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
G
50
|
T
T
G
G
T
T
R
R
F
F
G
G
T
T
D
D
L
L
A
A
60
|
K
K
E
E
A
A
K
K
K
K
V
V
H
H
Q
Q
T
T
T
T
70
|
R
R
T
T
V
V
P
P
A
A
K
K
R
R
G
G
T
T
I
I
80
|
Y
Y
D
D
R
R
N
N
G
G
V
V
P
P
I
I
A
A
E
E
90
|
D
D
A
A
T
T
S
S
Y
Y
N
N
V
V
Y
Y
A
A
V
V
100
|
I
I
D
D
E
E
N
N
Y
Y
K
K
S
S
A
A
T
T
G
G
110
|
K
K
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
V
V
E
E
K
K
T
T
Q
Q
F
F
120
|
N
N
K
K
V
V
A
A
E
E
V
V
F
F
H
H
K
K
Y
Y
130
|
L
L
D
D
M
M
E
E
E
E
S
S
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
140
|
Q
Q
L
L
S
S
Q
Q
P
P
N
N
L
L
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
150
|
S
S
F
F
G
G
A
A
K
K
G
G
N
N
G
G
I
I
T
T
160
|
Y
Y
A
A
N
N
M
M
M
M
S
S
I
I
K
K
K
K
E
E
170
|
L
L
E
E
A
A
A
A
E
E
V
V
K
K
G
G
I
I
D
D
180
|
F
F
T
T
T
T
S
S
P
P
N
N
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
P
P
190
|
N
N
G
G
Q
Q
F
F
A
A
S
S
S
S
F
F
I
I
G
G
200
|
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
H
H
E
E
N
N
E
E
D
D
G
G
210
|
S
S
K
K
S
S
L
L
L
L
G
G
T
T
S
S
G
G
M
M
220
|
E
E
S
S
S
S
L
L
N
N
S
S
I
I
L
L
A
A
G
G
230
|
T
T
D
D
G
G
I
I
I
I
T
T
Y
Y
E
E
K
K
D
D
240
|
R
R
L
L
G
G
N
N
I
I
V
V
P
P
G
G
T
T
E
E
250
|
Q
Q
V
V
S
S
Q
Q
R
R
T
T
M
M
D
D
G
G
K
K
260
|
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
T
T
T
T
I
I
S
S
S
S
P
P
L
L
270
|
Q
Q
S
S
F
F
M
M
E
E
T
T
Q
Q
M
M
D
D
A
A
280
|
F
F
Q
Q
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
G
G
K
K
Y
Y
M
M
290
|
T
T
A
A
T
T
L
L
V
V
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
G
G
300
|
E
E
I
I
L
L
A
A
T
T
T
T
Q
Q
R
R
P
P
T
T
310
|
F
F
D
D
A
A
D
D
T
T
K
K
E
E
G
G
I
I
T
T
320
|
E
E
D
D
F
F
V
V
W
W
R
R
D
D
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
330
|
Q
Q
S
S
N
N
Y
Y
E
E
P
P
G
G
S
S
T
A
M
F
340
|
K
K
V
V
M
M
M
M
L
L
A
A
A
A
A
A
I
I
D
D
350
|
N
N
N
N
T
T
F
F
P
P
G
G
G
G
E
E
V
V
F
F
360
|
N
N
S
S
S
S
E
E
L
L
K
K
I
I
A
A
D
D
A
A
370
|
T
T
I
I
R
R
D
D
W
W
D
D
V
V
N
N
E
E
G
G
380
|
L
L
T
T
G
G
G
G
R
R
M
M
M
M
T
T
F
F
S
S
390
|
Q
Q
G
G
F
F
A
A
H
H
S
S
S
S
N
N
V
V
G
G
400
|
M
M
T
T
L
L
L
L
E
E
Q
Q
K
K
M
M
G
G
D
D
410
|
A
A
T
T
W
W
L
L
D
D
Y
Y
L
L
N
N
R
R
F
F
420
|
K
K
F
F
G
G
V
V
P
P
T
T
R
R
F
F
G
G
L
L
430
|
T
T
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
A
A
G
G
Q
Q
L
L
P
P
A
A
440
|
D
D
N
N
I
I
V
V
N
N
I
I
A
A
Q
Q
S
S
S
S
450
|
F
F
G
G
Q
Q
G
G
I
I
S
S
V
V
T
T
Q
Q
T
T
460
|
Q
Q
M
M
I
I
R
R
A
A
F
F
T
T
A
A
I
I
A
A
470
|
N
N
D
D
G
G
V
V
M
M
L
L
E
E
P
P
K
K
F
F
480
|
I
I
S
S
A
A
I
I
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
N
N
D
D
Q
Q
490
|
T
T
A
A
R
R
K
K
S
S
Q
Q
K
K
E
E
I
I
V
V
500
|
G
G
N
N
P
P
V
V
S
S
K
K
D
D
A
A
A
A
S
S
510
|
L
L
T
T
R
R
T
T
N
N
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
520
|
T
T
D
D
P
P
V
V
Y
Y
G
G
T
T
M
M
Y
Y
N
N
530
|
H
H
S
S
T
T
G
G
K
K
P
P
T
T
V
V
T
T
V
V
540
|
P
P
G
G
Q
Q
N
N
V
V
A
A
L
L
K
K
S
S
G
G
550
|
T
T
A
A
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
D
D
E
E
K
K
N
N
G
G
560
|
G
G
Y
Y
L
L
V
V
G
G
L
L
T
T
D
D
Y
Y
I
I
570
|
F
F
S
S
A
A
V
V
S
S
M
M
S
S
P
P
A
A
E
E
580
|
N
N
P
P
D
D
F
F
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
V
V
T
T
V
V
590
|
Q
Q
Q
Q
P
P
E
E
H
H
Y
Y
S
S
G
G
I
I
Q
Q
600
|
L
L
G
G
E
E
F
F
A
A
N
N
P
P
I
I
L
L
E
E
610
|
R
R
A
A
S
S
A
A
M
M
K
K
D
D
S
S
L
L
N
N
620
|
L
L
Q
Q
T
T
T
T
A
A
K
K
A
A
L
L
E
E
Q
Q
630
|
V
V
S
S
Q
Q
Q
Q
S
S
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
M
M
P
P
640
|
S
S
V
V
K
K
D
D
I
I
S
S
P
P
G
G
D
D
L
L
650
|
A
A
E
E
E
E
L
L
R
R
R
R
N
N
L
L
V
V
Q
Q
660
|
P
P
I
I
V
V
V
V
G
G
T
T
G
G
T
T
K
K
I
I
670
|
K
K
N
N
S
S
S
S
A
A
E
E
E
E
G
G
K
K
N
N
680
|
L
L
A
A
P
P
N
N
Q
Q
Q
Q
V
V
L
L
I
I
L
L
690
|
S
S
D
D
K
K
A
A
E
E
E
E
V
V
P
P
D
D
M
M
700
|
Y
Y
G
G
W
W
T
T
K
K
E
E
T
T
A
A
E
E
T
T
710
|
L
L
A
A
K
K
W
W
L
L
N
N
I
I
E
E
L
L
E
E
720
|
F
F
Q
Q
G
G
S
S
G
G
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
K
K
730
|
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
R
R
A
A
N
N
T
T
A
A
I
I
K
K
740
|
D
D
I
I
K
K
K
K
I
I
T
T
L
L
T
T
L
L
G
G
750
|
D
D
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates | 1313 | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Genome sequence assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Beta-Lactam resistance in S. pneumoniae is caused by mutations in the penicillin-binding domains of one or more of its six penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) resulting from point mutations or mosaic genes. Altered PBP 1a, PBP 2x, and PBP 2b are the most important PBPs for Beta-lactam resistance among clinical isolates. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Penicillin-binding protein 2X (PBP2X) | [1], [2], [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Community-acquired pneumonia [ICD-11: CA40.2] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.I371T |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates | 1313 | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Genome sequence assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Beta-Lactam resistance in S. pneumoniae is caused by mutations in the penicillin-binding domains of one or more of its six penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) resulting from point mutations or mosaic genes. Altered PBP 1a, PBP 2x, and PBP 2b are the most important PBPs for Beta-lactam resistance among clinical isolates. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Penicillin-binding protein 2X (PBP2X) | [1], [2], [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Community-acquired pneumonia [ICD-11: CA40.2] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R384G |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates | 1313 | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Genome sequence assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Beta-Lactam resistance in S. pneumoniae is caused by mutations in the penicillin-binding domains of one or more of its six penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) resulting from point mutations or mosaic genes. Altered PBP 1a, PBP 2x, and PBP 2b are the most important PBPs for Beta-lactam resistance among clinical isolates. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Penicillin-binding protein 2X (PBP2X) | [1], [2], [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Community-acquired pneumonia [ICD-11: CA40.2] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.M400T |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates | 1313 | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Genome sequence assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Beta-Lactam resistance in S. pneumoniae is caused by mutations in the penicillin-binding domains of one or more of its six penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) resulting from point mutations or mosaic genes. Altered PBP 1a, PBP 2x, and PBP 2b are the most important PBPs for Beta-lactam resistance among clinical isolates. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Penicillin-binding protein 2X (PBP2X) | [1], [2], [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Community-acquired pneumonia [ICD-11: CA40.2] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | STMK motif p.M>F |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates | 1313 | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Genome sequence assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Beta-Lactam resistance in S. pneumoniae is caused by mutations in the penicillin-binding domains of one or more of its six penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) resulting from point mutations or mosaic genes. Altered PBP 1a, PBP 2x, and PBP 2b are the most important PBPs for Beta-lactam resistance among clinical isolates. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Penicillin-binding protein 1A (PBP1A) | [1], [2], [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Community-acquired pneumonia [ICD-11: CA40.2] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | STMK motif p.T >A +SRNVP motif p.P >T |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates | 1313 | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Genome sequence assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Beta-Lactam resistance in S. pneumoniae is caused by mutations in the penicillin-binding domains of one or more of its six penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) resulting from point mutations or mosaic genes. Altered PBP 1a, PBP 2x, and PBP 2b are the most important PBPs for Beta-lactam resistance among clinical isolates. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Penicillin-binding protein 2B (PBP2B) | [1], [2], [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Community-acquired pneumonia [ICD-11: CA40.2] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.KTGTA motif p.A >G |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates | 1313 | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Genome sequence assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Beta-Lactam resistance in S. pneumoniae is caused by mutations in the penicillin-binding domains of one or more of its six penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) resulting from point mutations or mosaic genes. Altered PBP 1a, PBP 2x, and PBP 2b are the most important PBPs for Beta-lactam resistance among clinical isolates. | ||||||||||||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
