Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00149) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Chlorpheniramine
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Allergican; Allergisan; Antagonate; Chloropheniramine; Chlorophenylpyridamin; Chlorophenylpyridamine; Chloropiril; Chloroprophenpyridamine; Chlorphenamine; Chlorphenaminum; Chlorpheniraminum; Chlorprophenpyridamine; Clofeniramina; Clorfenamina; Clorfeniramina; Cloropiril; Haynon; Hayon; Histadur; ISOCLOR; Kloromin; Phenetron; PiriIton; Piriton; Polaronil; Telachlor; Teldrin; Chlorphenamine [INN]; Clorfeniramina [Italian]; Pediacare Allergy Formula; [3H]Chlorpheniramine; Aller-Chlor; Chlo-amine; Chlor-Pro; Chlor-Trimeton Repetabs; Chlor-trimeton; Chlorphenamine (INN); Chlorphenaminum [INN-Latin]; Clofeniramina (TN); Clorfenamina [INN-Spanish]; Comakin (TN); Gen-Allerate; Novo-Pheniram; Piriton (TN); Chlor-Trimeton (TN); Chlor-Tripolon (TN); CHLORPHENIRAMINE (SEE ALSO: CHLORPHENIRAMINE MALEATE (CAS113-92-8)); Gamma-(4-Chlorophenyl)-gamma-(2-pyridyl)propyldimethylamine; Gamma-(4-Chlorophenyl)-N,N-dimethyl-2-pyridinepropanamine; 1-(p-Chlorophenyl)-1-(2-pyridyl)-3-N,N-dimethylpropylamine; 1-(p-Chlorophenyl)-1-(2-pyridyl)-3-dimethylaminopropane; 2-(p-Chloro-alpha-(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)benzyl)pyridine; 3-(4-chlorophenyl)-N,N-dimethyl-3-(pyridin-2-yl)propan-1-amine; 3-(4-chlorophenyl)-N,N-dimethyl-3-pyridin-2-ylpropan-1-amine; 3-(p-Chlorophenyl)-3-(2-pyridyl)-N,N-dimethylpropylamine; 4-Chloropheniramine
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
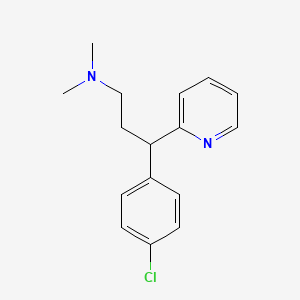
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Histamine H1 receptor (H1R) | HRH1_HUMAN | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C16H19ClN2
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CN(C)CCC(C1=CC=C(C=C1)Cl)C2=CC=CC=N2
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C16H19ClN2/c1-19(2)12-10-15(16-5-3-4-11-18-16)13-6-8-14(17)9-7-13/h3-9,11,15H,10,12H2,1-2H3
|
||||
| InChIKey |
SOYKEARSMXGVTM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Chloroquine resistance transporter (CRT) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Malaria [ICD-11: 1F45.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K76N |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasmodium falciparum | 5833 | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Malaria SYBR Green I-based fluorescence (MSF) method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mutations within PfCRT, particularly changes from a charged amino acid residue (lysine, k76) to an uncharged residue (such as threonine [76T], asparagine [76N], or isoleucine [76I]), seem to be important not only in the acquisition of resistance to quinoline antimalarials (e.g., by allowing efflux of diprotic CQ), but also in the mechanism of resistance reversal actions for chemosens. | |||
| Key Molecule: Chloroquine resistance transporter (CRT) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Malaria [ICD-11: 1F45.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K76T |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasmodium falciparum | 5833 | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Malaria SYBR Green I-based fluorescence (MSF) method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mutations within PfCRT, particularly changes from a charged amino acid residue (lysine, k76) to an uncharged residue (such as threonine [76T], asparagine [76N], or isoleucine [76I]), seem to be important not only in the acquisition of resistance to quinoline antimalarials (e.g., by allowing efflux of diprotic CQ), but also in the mechanism of resistance reversal actions for chemosens. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
