Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00082) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Tesevatinib
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Tesevatinib; XL647; XL-647; 781613-23-8; EXEL-7647; UNII-F6XM2TN5A1; KD-019; XL 647; F6XM2TN5A1; 651031-01-5; 7-[[(3aS,6aR)-2-methyl-3,3a,4,5,6,6a-hexahydro-1H-cyclopenta[c]pyrrol-5-yl]methoxy]-N-(3,4-dichloro-2-fluorophenyl)-6-methoxyquinazolin-4-amine; Tesevatinib [USAN:INN]; EXEL 7647; 874286-84-7; KD 019; 1000599-06-3; SCHEMBL721994; SCHEMBL721993; SCHEMBL721992; C24H25Cl2FN4O2; GTPL7944; CHEMBL3544983; EX-A172; QCR-153; MolPort-044-724-458; BCP23438; ZINC38912363; 2809AH; AKOS027255007
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 5 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
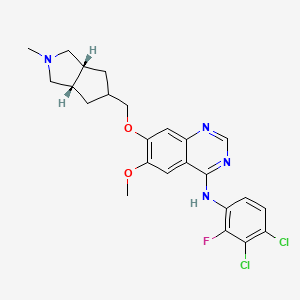
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Ephrin type-B receptor 4 (EPHB4) | EPHB4_HUMAN | [1] | ||
| Tyrosine-protein kinase (PTK) | NOUNIPROTAC | [1] | |||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C24H25Cl2FN4O2
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CN1C[C@H]2CC(C[C@H]2C1)COC3=C(C=C4C(=C3)N=CN=C4NC5=C(C(=C(C=C5)Cl)Cl)F)OC
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C24H25Cl2FN4O2/c1-31-9-14-5-13(6-15(14)10-31)11-33-21-8-19-16(7-20(21)32-2)24(29-12-28-19)30-18-4-3-17(25)22(26)23(18)27/h3-4,7-8,12-15H,5-6,9-11H2,1-2H3,(H,28,29,30)/t13 ,14-,15+
|
||||
| InChIKey |
HVXKQKFEHMGHSL-GOOCMWNKSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T790M |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.05 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
S
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
M
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
C
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
Q
Q
G
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Direct sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The most common mechanism of acquired resistance is caused by the development of the T790M mutation in exon 20 of EGFR in nearly 50% of patients, whereas 10% of the patients have amplification of the oncogene MET as a means of resistance. | ||||||||||||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
