Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00078) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Cefixime
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
CFIX; Cefixima; Cefiximum; Denvar; Necopen; Tricef; CL-284635; FK-027; FR-17027; Ofex (TN); Suprax (TN); Cefixime (JP15/USP/INN); (6R,7R)-7-({(2Z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-[(carboxymethoxy)imino]acetyl}amino)-3-ethenyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid; (6R,7R)-7-[[(2Z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-(carboxymethyloxyimino)acetyl]amino]-3-ethenyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid; (6R,7R)-7-{[(2Z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-{[(carboxymethyl)oxy]imino}acetyl]amino}-3-ethenyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid; (6r,7r)-7-[-2-(2-amino-thiazol-4-yl)-2-carboxymethoxyimino-acetylamino]-8-oxo-3-vinyl-5-thia-1-aza-b; 7beta-{(2Z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-[(carboxymethoxy)imino]acetamido}-3-ethenyl-3,4-didehydrocepham-4-carboxylic acid
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
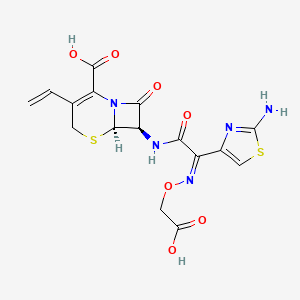
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(2 diseases)
[7]
|
||||
| Target | Bacterial Penicillin binding protein (Bact PBP) | NOUNIPROTAC | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C16H15N5O7S2
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C=CC1=C(N2[C@@H]([C@@H](C2=O)NC(=O)/C(=N\\OCC(=O)O)/C3=CSC(=N3)N)SC1)C(=O)O
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C16H15N5O7S2/c1-2-6-4-29-14-10(13(25)21(14)11(6)15(26)27)19-12(24)9(20-28-3-8(22)23)7-5-30-16(17)18-7/h2,5,10,14H,1,3-4H2,(H2,17,18)(H,19,24)(H,22,23)(H,26,27)/b20-9-/t10-,14-/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
OKBVVJOGVLARMR-QSWIMTSFSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Probable peptidoglycan D,D-transpeptidase PenA (PENA) | [1], [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gonococcal infection [ICD-11: 1A70.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A311V |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Neisseria gonorrhoeae FA19 | 528352 | ||
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae FA6140 | 528353 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay; broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The penA gene,which encodes penicillin-binding protein 2 (PBP2), from H041 (penA41) is a mosaic penA allele similar to mosaic alleles conferring intermediate-level cephalosporin resistance.Tthree novel mutations, A311V, V316P, and T483S, that, when incorporated into the mosaic penA35 allele, are responsible for essentially all of the additional resistance conferred by penA41. Two of these mutations, A311V and T316P, are located near the active-site nucleophile Ser310, in a region previously shown to harbor mutations that increase resistance, whereas the remaining mutation, T483S, is in a different location in the structure of PBP2, where it may interact with the Beta-lactam carboxylate. | |||
| Key Molecule: Probable peptidoglycan D,D-transpeptidase PenA (PENA) | [1], [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gonococcal infection [ICD-11: 1A70.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T316P |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Neisseria gonorrhoeae FA19 | 528352 | ||
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae FA6140 | 528353 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay; broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The penA gene,which encodes penicillin-binding protein 2 (PBP2), from H041 (penA41) is a mosaic penA allele similar to mosaic alleles conferring intermediate-level cephalosporin resistance.Tthree novel mutations, A311V, V316P, and T483S, that, when incorporated into the mosaic penA35 allele, are responsible for essentially all of the additional resistance conferred by penA41. Two of these mutations, A311V and T316P, are located near the active-site nucleophile Ser310, in a region previously shown to harbor mutations that increase resistance, whereas the remaining mutation, T483S, is in a different location in the structure of PBP2, where it may interact with the Beta-lactam carboxylate. | |||
| Key Molecule: Probable peptidoglycan D,D-transpeptidase PenA (PENA) | [1], [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gonococcal infection [ICD-11: 1A70.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A311V+p.T316P |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Neisseria gonorrhoeae FA19 | 528352 | ||
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae FA6140 | 528353 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay; broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The penA gene,which encodes penicillin-binding protein 2 (PBP2), from H041 (penA41) is a mosaic penA allele similar to mosaic alleles conferring intermediate-level cephalosporin resistance.Tthree novel mutations, A311V, V316P, and T483S, that, when incorporated into the mosaic penA35 allele, are responsible for essentially all of the additional resistance conferred by penA41. Two of these mutations, A311V and T316P, are located near the active-site nucleophile Ser310, in a region previously shown to harbor mutations that increase resistance, whereas the remaining mutation, T483S, is in a different location in the structure of PBP2, where it may interact with the Beta-lactam carboxylate. | |||
| Key Molecule: Probable peptidoglycan D,D-transpeptidase PenA (PENA) | [1], [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gonococcal infection [ICD-11: 1A70.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T483S |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Neisseria gonorrhoeae FA19 | 528352 | ||
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae FA6140 | 528353 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay; broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The penA gene,which encodes penicillin-binding protein 2 (PBP2), from H041 (penA41) is a mosaic penA allele similar to mosaic alleles conferring intermediate-level cephalosporin resistance.Tthree novel mutations, A311V, V316P, and T483S, that, when incorporated into the mosaic penA35 allele, are responsible for essentially all of the additional resistance conferred by penA41. Two of these mutations, A311V and T316P, are located near the active-site nucleophile Ser310, in a region previously shown to harbor mutations that increase resistance, whereas the remaining mutation, T483S, is in a different location in the structure of PBP2, where it may interact with the Beta-lactam carboxylate. | |||
| Key Molecule: Probable peptidoglycan D,D-transpeptidase PenA (PENA) | [1], [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gonococcal infection [ICD-11: 1A70.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T483S+p.A311V+p.T316P |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Neisseria gonorrhoeae FA19 | 528352 | ||
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae FA6140 | 528353 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay; broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The penA gene,which encodes penicillin-binding protein 2 (PBP2), from H041 (penA41) is a mosaic penA allele similar to mosaic alleles conferring intermediate-level cephalosporin resistance.Tthree novel mutations, A311V, V316P, and T483S, that, when incorporated into the mosaic penA35 allele, are responsible for essentially all of the additional resistance conferred by penA41. Two of these mutations, A311V and T316P, are located near the active-site nucleophile Ser310, in a region previously shown to harbor mutations that increase resistance, whereas the remaining mutation, T483S, is in a different location in the structure of PBP2, where it may interact with the Beta-lactam carboxylate. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
