Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00064) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Rifabutin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Alfacid; Ansamycin; Ansatipin; Ansatipine; Assatipin; Mycobutin; RBT; Rifabutina; Rifabutine; Rifabutinum; Grunenthal Brand of Rifabutin; Kenfarma Brand of Rifabutin; Pfizer Brand of Rifabutin; Rifabutin Pfizer Brand; Rifabutina [Spanish]; Rifabutine [French]; Rifabutinum [Latin]; Antibiotic LM 427; LM 427; LM427; DRG-0085; LM-427; Mycobutin (TN); Rifabutin [USAN:BAN:INN]; Rifabutin (JAN/USP/INN); Mycobutin, Ansamycin, LM 427, Ansatipine, Rifabutin; (9S,12E,14S,15R,16S,17R,18R,19R,20S,21S,22E,24Z)-6,18,20-trihydroxy-1'-isobutyl-14-methoxy-7,9,15,17,19,21,25-heptamethyl-5,10,26-trioxo-3,5,9,10-tetrahydrospiro[9,4-(epoxypentadeca[1,11,13]trienoimino)furo[2',3':7,8]naphtho[1,2-d]imidazole-2,4'-piperidin; Spiro[9,4-(epoxypentadeca[1,11,13]trienimino)-2H-furo[2',3':7,8]naphth[1,2-d]imidazole-2,4'-piperidine]-5,10,26(3H,9H)-trione, 16-(acetyloxy)-6,18,20-trihydroxy-14-methoxy-7,9,15,17,19,21,25-heptameth; 1,4-Dihydro-1-deoxy-1',4-didehydro-5'-(2-methylpropyl)-1-oxorifamycin XIV; 4-Deoxo-3,4-(2-spiro(N-isobutyl-4-piperidyl)-2,5-dihydro-1H-imidazo)-rifamycin S; 4-N-isobutylspiropiperidylrifamycin S
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 2 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
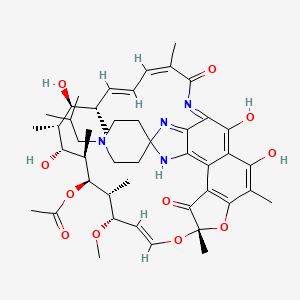
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[2]
|
||||
| Target | DNA-directed RNA polymerase (RNAP) | NOUNIPROTAC | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C46H62N4O11
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C[C@H]1/C=C/C=C(\\C(=O)N=C2C(=C3C(=C4C2=NC5(N4)CCN(CC5)CC(C)C)C6=C(C(=C3O)C)O[C@@](C6=O)(O/C=C/[C@@H]([C@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H]1O)C)O)C)OC(=O)C)C)OC)C)O)/C
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C46H62N4O11/c1-22(2)21-50-18-16-46(17-19-50)48-34-31-32-39(54)28(8)42-33(31)43(56)45(10,61-42)59-20-15-30(58-11)25(5)41(60-29(9)51)27(7)38(53)26(6)37(52)23(3)13-12-14-24(4)44(57)47-36(40(32)55)35(34)49-46/h12-15,20,22-23,25-27,30,37-38,41,48,52-55H,16-19,21H2,1-11H3/b13-12+,20-15+,24-14-,47-36 /t23-,25+,26+,27+,30-,37-,38+,41+,45-/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
ZWBTYMGEBZUQTK-PVLSIAFMSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Outer membrane protein A (OmpA) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Tuberculosis [ICD-11: 1B10.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expressiom | D538G+Y537S+Y537N+E380Q |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Mycobacterium tuberculosis | 1773 | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | These results support the model that the roles of OmpA as a porin protein overexpressing in mycobacteria can increase the hydrophilic ability of the cell wall which can facilitate the streptomycin uptakes and increase the mycobacteria's sensitivity to aminoglycosides. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.H481N |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain T109 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T112 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T113 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T115 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T118 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T124 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T161 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T166 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T20 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T211 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T212 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T236 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aac | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T248 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T249 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T25 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T250 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T262 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T264 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T295 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T296 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T297 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T36 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T382 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T397 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T398 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T399 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T4 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T400 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T401 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T402 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T403 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T404 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T46 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T59 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T66 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Twelve mutational changes at 10 positions were identified, with 473Ala-Thr representing a new mutation site. New amino acid substitutions, 465Gln-Arg, 466Leu-Ser, 468Gln-Lys, and 477Ala-Thr in cluster I and 527Ile-Met and 529Ser-Leu in cluster II, were described, thereby emphasizing the high variability of these amino acid positions. Codon 481 was mutated on 32 separate occasions, which indicates a central role of this amino acid. All in vivo isolates that demonstrated two or three amino acid changes exhibited high-level resistance. Interestingly enough, all of these isolates showed the mutational change 481His-Asn, which is capable of conferring low-level resistance on its own, thereby indicating a two-step resistance mechanism in vivo to high-level resistance within these isolates. High-level resistance in vivo, however, was not demonstrated to occur through multiple mutations alone. The single amino acid substitution 468Gln-Lys also causes high-level resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A473T |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain T109 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T112 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T113 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T115 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T118 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T124 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T161 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T166 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T20 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T211 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T212 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T236 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aac | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T248 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T249 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T25 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T250 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T262 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T264 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T295 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T296 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T297 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T36 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T382 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T397 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T398 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T399 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T4 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T400 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T401 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T402 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T403 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T404 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T46 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T59 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T66 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Twelve mutational changes at 10 positions were identified, with 473Ala-Thr representing a new mutation site. New amino acid substitutions, 465Gln-Arg, 466Leu-Ser, 468Gln-Lys, and 477Ala-Thr in cluster I and 527Ile-Met and 529Ser-Leu in cluster II, were described, thereby emphasizing the high variability of these amino acid positions. Codon 481 was mutated on 32 separate occasions, which indicates a central role of this amino acid. All in vivo isolates that demonstrated two or three amino acid changes exhibited high-level resistance. Interestingly enough, all of these isolates showed the mutational change 481His-Asn, which is capable of conferring low-level resistance on its own, thereby indicating a two-step resistance mechanism in vivo to high-level resistance within these isolates. High-level resistance in vivo, however, was not demonstrated to occur through multiple mutations alone. The single amino acid substitution 468Gln-Lys also causes high-level resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q465R |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain T109 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T112 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T113 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T115 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T118 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T124 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T161 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T166 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T20 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T211 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T212 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T236 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aac | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T248 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T249 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T25 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T250 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T262 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T264 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T295 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T296 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T297 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T36 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T382 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T397 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T398 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T399 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T4 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T400 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T401 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T402 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T403 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T404 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T46 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T59 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T66 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Twelve mutational changes at 10 positions were identified, with 473Ala-Thr representing a new mutation site. New amino acid substitutions, 465Gln-Arg, 466Leu-Ser, 468Gln-Lys, and 477Ala-Thr in cluster I and 527Ile-Met and 529Ser-Leu in cluster II, were described, thereby emphasizing the high variability of these amino acid positions. Codon 481 was mutated on 32 separate occasions, which indicates a central role of this amino acid. All in vivo isolates that demonstrated two or three amino acid changes exhibited high-level resistance. Interestingly enough, all of these isolates showed the mutational change 481His-Asn, which is capable of conferring low-level resistance on its own, thereby indicating a two-step resistance mechanism in vivo to high-level resistance within these isolates. High-level resistance in vivo, however, was not demonstrated to occur through multiple mutations alone. The single amino acid substitution 468Gln-Lys also causes high-level resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L466S |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain T109 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T112 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T113 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T115 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T118 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T124 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T161 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T166 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T20 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T211 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T212 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T236 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aac | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T248 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T249 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T25 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T250 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T262 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T264 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T295 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T296 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T297 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T36 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T382 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T397 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T398 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T399 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T4 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T400 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T401 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T402 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T403 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T404 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T46 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T59 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T66 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Twelve mutational changes at 10 positions were identified, with 473Ala-Thr representing a new mutation site. New amino acid substitutions, 465Gln-Arg, 466Leu-Ser, 468Gln-Lys, and 477Ala-Thr in cluster I and 527Ile-Met and 529Ser-Leu in cluster II, were described, thereby emphasizing the high variability of these amino acid positions. Codon 481 was mutated on 32 separate occasions, which indicates a central role of this amino acid. All in vivo isolates that demonstrated two or three amino acid changes exhibited high-level resistance. Interestingly enough, all of these isolates showed the mutational change 481His-Asn, which is capable of conferring low-level resistance on its own, thereby indicating a two-step resistance mechanism in vivo to high-level resistance within these isolates. High-level resistance in vivo, however, was not demonstrated to occur through multiple mutations alone. The single amino acid substitution 468Gln-Lys also causes high-level resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q468K |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain T109 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T112 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T113 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T115 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T118 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T124 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T161 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T166 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T20 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T211 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T212 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T236 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aac | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T248 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T249 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T25 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T250 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T262 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T264 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T295 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T296 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T297 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T36 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T382 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T397 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T398 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T399 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T4 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T400 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T401 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T402 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T403 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T404 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T46 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T59 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T66 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Twelve mutational changes at 10 positions were identified, with 473Ala-Thr representing a new mutation site. New amino acid substitutions, 465Gln-Arg, 466Leu-Ser, 468Gln-Lys, and 477Ala-Thr in cluster I and 527Ile-Met and 529Ser-Leu in cluster II, were described, thereby emphasizing the high variability of these amino acid positions. Codon 481 was mutated on 32 separate occasions, which indicates a central role of this amino acid. All in vivo isolates that demonstrated two or three amino acid changes exhibited high-level resistance. Interestingly enough, all of these isolates showed the mutational change 481His-Asn, which is capable of conferring low-level resistance on its own, thereby indicating a two-step resistance mechanism in vivo to high-level resistance within these isolates. High-level resistance in vivo, however, was not demonstrated to occur through multiple mutations alone. The single amino acid substitution 468Gln-Lys also causes high-level resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D471Y |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain T109 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T112 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T113 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T115 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T118 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T124 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T161 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T166 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T20 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T211 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T212 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T236 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aac | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T248 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T249 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T25 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T250 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T262 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T264 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T295 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T296 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T297 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T36 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T382 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T397 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T398 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T399 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T4 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T400 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T401 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T402 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T403 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T404 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T46 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T59 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T66 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Twelve mutational changes at 10 positions were identified, with 473Ala-Thr representing a new mutation site. New amino acid substitutions, 465Gln-Arg, 466Leu-Ser, 468Gln-Lys, and 477Ala-Thr in cluster I and 527Ile-Met and 529Ser-Leu in cluster II, were described, thereby emphasizing the high variability of these amino acid positions. Codon 481 was mutated on 32 separate occasions, which indicates a central role of this amino acid. All in vivo isolates that demonstrated two or three amino acid changes exhibited high-level resistance. Interestingly enough, all of these isolates showed the mutational change 481His-Asn, which is capable of conferring low-level resistance on its own, thereby indicating a two-step resistance mechanism in vivo to high-level resistance within these isolates. High-level resistance in vivo, however, was not demonstrated to occur through multiple mutations alone. The single amino acid substitution 468Gln-Lys also causes high-level resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A477T |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain T109 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T112 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T113 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T115 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T118 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T124 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T161 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T166 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T20 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T211 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T212 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T236 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aac | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T248 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T249 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T25 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T250 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T262 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T264 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T295 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T296 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T297 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T36 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T382 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T397 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T398 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T399 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T4 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T400 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T401 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T402 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T403 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T404 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T46 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T59 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T66 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Twelve mutational changes at 10 positions were identified, with 473Ala-Thr representing a new mutation site. New amino acid substitutions, 465Gln-Arg, 466Leu-Ser, 468Gln-Lys, and 477Ala-Thr in cluster I and 527Ile-Met and 529Ser-Leu in cluster II, were described, thereby emphasizing the high variability of these amino acid positions. Codon 481 was mutated on 32 separate occasions, which indicates a central role of this amino acid. All in vivo isolates that demonstrated two or three amino acid changes exhibited high-level resistance. Interestingly enough, all of these isolates showed the mutational change 481His-Asn, which is capable of conferring low-level resistance on its own, thereby indicating a two-step resistance mechanism in vivo to high-level resistance within these isolates. High-level resistance in vivo, however, was not demonstrated to occur through multiple mutations alone. The single amino acid substitution 468Gln-Lys also causes high-level resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.I527M |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain T109 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T112 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T113 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T115 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T118 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T124 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T161 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T166 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T20 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T211 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T212 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T236 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aac | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T248 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T249 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T25 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T250 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T262 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T264 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T295 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T296 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T297 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T36 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T382 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T397 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T398 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T399 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T4 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T400 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T401 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T402 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T403 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T404 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T46 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T59 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T66 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Twelve mutational changes at 10 positions were identified, with 473Ala-Thr representing a new mutation site. New amino acid substitutions, 465Gln-Arg, 466Leu-Ser, 468Gln-Lys, and 477Ala-Thr in cluster I and 527Ile-Met and 529Ser-Leu in cluster II, were described, thereby emphasizing the high variability of these amino acid positions. Codon 481 was mutated on 32 separate occasions, which indicates a central role of this amino acid. All in vivo isolates that demonstrated two or three amino acid changes exhibited high-level resistance. Interestingly enough, all of these isolates showed the mutational change 481His-Asn, which is capable of conferring low-level resistance on its own, thereby indicating a two-step resistance mechanism in vivo to high-level resistance within these isolates. High-level resistance in vivo, however, was not demonstrated to occur through multiple mutations alone. The single amino acid substitution 468Gln-Lys also causes high-level resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S529L |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain T109 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T112 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T113 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T115 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T118 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T124 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T161 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T166 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T20 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T211 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T212 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T236 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aac | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T248 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T249 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T25 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T250 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T262 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T264 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T295 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T296 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T297 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T36 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T382 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T397 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T398 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T399 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T4 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T400 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T401 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T402 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T403 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T404 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T46 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T59 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T66 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Twelve mutational changes at 10 positions were identified, with 473Ala-Thr representing a new mutation site. New amino acid substitutions, 465Gln-Arg, 466Leu-Ser, 468Gln-Lys, and 477Ala-Thr in cluster I and 527Ile-Met and 529Ser-Leu in cluster II, were described, thereby emphasizing the high variability of these amino acid positions. Codon 481 was mutated on 32 separate occasions, which indicates a central role of this amino acid. All in vivo isolates that demonstrated two or three amino acid changes exhibited high-level resistance. Interestingly enough, all of these isolates showed the mutational change 481His-Asn, which is capable of conferring low-level resistance on its own, thereby indicating a two-step resistance mechanism in vivo to high-level resistance within these isolates. High-level resistance in vivo, however, was not demonstrated to occur through multiple mutations alone. The single amino acid substitution 468Gln-Lys also causes high-level resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.H481N+p.L466S |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain T109 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T112 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T113 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T115 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T118 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T124 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T161 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T166 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T20 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T211 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T212 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T236 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aac | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T248 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T249 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T25 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T250 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T262 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T264 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T295 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T296 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T297 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T36 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T382 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T397 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T398 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T399 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T4 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T400 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T401 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T402 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T403 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T404 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T46 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T59 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T66 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Twelve mutational changes at 10 positions were identified, with 473Ala-Thr representing a new mutation site. New amino acid substitutions, 465Gln-Arg, 466Leu-Ser, 468Gln-Lys, and 477Ala-Thr in cluster I and 527Ile-Met and 529Ser-Leu in cluster II, were described, thereby emphasizing the high variability of these amino acid positions. Codon 481 was mutated on 32 separate occasions, which indicates a central role of this amino acid. All in vivo isolates that demonstrated two or three amino acid changes exhibited high-level resistance. Interestingly enough, all of these isolates showed the mutational change 481His-Asn, which is capable of conferring low-level resistance on its own, thereby indicating a two-step resistance mechanism in vivo to high-level resistance within these isolates. High-level resistance in vivo, however, was not demonstrated to occur through multiple mutations alone. The single amino acid substitution 468Gln-Lys also causes high-level resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.H481N+p.S529L |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain T109 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T112 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T113 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T115 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T118 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T124 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T161 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T166 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T20 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T211 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T212 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T236 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aac | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T248 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T249 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T25 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T250 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T262 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T264 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T295 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T296 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T297 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T36 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T382 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T397 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T398 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T399 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T4 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T400 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T401 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T402 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T403 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T404 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T46 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T59 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T66 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Twelve mutational changes at 10 positions were identified, with 473Ala-Thr representing a new mutation site. New amino acid substitutions, 465Gln-Arg, 466Leu-Ser, 468Gln-Lys, and 477Ala-Thr in cluster I and 527Ile-Met and 529Ser-Leu in cluster II, were described, thereby emphasizing the high variability of these amino acid positions. Codon 481 was mutated on 32 separate occasions, which indicates a central role of this amino acid. All in vivo isolates that demonstrated two or three amino acid changes exhibited high-level resistance. Interestingly enough, all of these isolates showed the mutational change 481His-Asn, which is capable of conferring low-level resistance on its own, thereby indicating a two-step resistance mechanism in vivo to high-level resistance within these isolates. High-level resistance in vivo, however, was not demonstrated to occur through multiple mutations alone. The single amino acid substitution 468Gln-Lys also causes high-level resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.H481N+p.I527M |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain T109 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T112 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T113 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T115 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T118 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T124 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T161 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T166 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T20 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T211 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T212 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T236 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aac | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T248 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T249 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T25 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T250 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T262 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T264 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T295 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T296 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T297 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T36 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T382 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T397 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T398 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T399 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T4 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T400 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T401 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T402 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T403 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T404 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T46 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T59 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T66 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Twelve mutational changes at 10 positions were identified, with 473Ala-Thr representing a new mutation site. New amino acid substitutions, 465Gln-Arg, 466Leu-Ser, 468Gln-Lys, and 477Ala-Thr in cluster I and 527Ile-Met and 529Ser-Leu in cluster II, were described, thereby emphasizing the high variability of these amino acid positions. Codon 481 was mutated on 32 separate occasions, which indicates a central role of this amino acid. All in vivo isolates that demonstrated two or three amino acid changes exhibited high-level resistance. Interestingly enough, all of these isolates showed the mutational change 481His-Asn, which is capable of conferring low-level resistance on its own, thereby indicating a two-step resistance mechanism in vivo to high-level resistance within these isolates. High-level resistance in vivo, however, was not demonstrated to occur through multiple mutations alone. The single amino acid substitution 468Gln-Lys also causes high-level resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.H481N+p.S529L+p.Q465R |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain T109 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T112 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T113 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T115 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T118 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T124 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T161 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T166 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T20 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T211 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T212 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T236 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aac | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T248 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T249 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T25 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T250 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T262 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T264 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T295 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T296 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T297 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T36 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T382 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T397 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T398 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T399 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T4 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T400 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T401 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T402 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T403 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T404 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T46 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T59 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T66 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Twelve mutational changes at 10 positions were identified, with 473Ala-Thr representing a new mutation site. New amino acid substitutions, 465Gln-Arg, 466Leu-Ser, 468Gln-Lys, and 477Ala-Thr in cluster I and 527Ile-Met and 529Ser-Leu in cluster II, were described, thereby emphasizing the high variability of these amino acid positions. Codon 481 was mutated on 32 separate occasions, which indicates a central role of this amino acid. All in vivo isolates that demonstrated two or three amino acid changes exhibited high-level resistance. Interestingly enough, all of these isolates showed the mutational change 481His-Asn, which is capable of conferring low-level resistance on its own, thereby indicating a two-step resistance mechanism in vivo to high-level resistance within these isolates. High-level resistance in vivo, however, was not demonstrated to occur through multiple mutations alone. The single amino acid substitution 468Gln-Lys also causes high-level resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.H481N+p.A473T+p.A477T |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain T109 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T112 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T113 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T115 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T118 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T124 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T161 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T166 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T20 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T211 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T212 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T236 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aac | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T248 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T249 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T25 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T250 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T262 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T264 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T295 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T296 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T297 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T36 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T382 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T397 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T398 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T399 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T4 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T400 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T401 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T402 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T403 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T404 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T46 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T59 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T66 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Twelve mutational changes at 10 positions were identified, with 473Ala-Thr representing a new mutation site. New amino acid substitutions, 465Gln-Arg, 466Leu-Ser, 468Gln-Lys, and 477Ala-Thr in cluster I and 527Ile-Met and 529Ser-Leu in cluster II, were described, thereby emphasizing the high variability of these amino acid positions. Codon 481 was mutated on 32 separate occasions, which indicates a central role of this amino acid. All in vivo isolates that demonstrated two or three amino acid changes exhibited high-level resistance. Interestingly enough, all of these isolates showed the mutational change 481His-Asn, which is capable of conferring low-level resistance on its own, thereby indicating a two-step resistance mechanism in vivo to high-level resistance within these isolates. High-level resistance in vivo, however, was not demonstrated to occur through multiple mutations alone. The single amino acid substitution 468Gln-Lys also causes high-level resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D471Y+p.S486L |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain T109 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T112 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T113 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T115 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T118 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T124 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T161 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T166 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T20 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T211 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T212 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T236 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aac | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T248 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T249 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T25 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T250 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T262 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T264 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T295 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T296 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T297 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T36 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T382 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T397 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T398 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T399 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T4 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T400 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T401 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T402 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T403 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T404 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T46 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T59 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T66 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Twelve mutational changes at 10 positions were identified, with 473Ala-Thr representing a new mutation site. New amino acid substitutions, 465Gln-Arg, 466Leu-Ser, 468Gln-Lys, and 477Ala-Thr in cluster I and 527Ile-Met and 529Ser-Leu in cluster II, were described, thereby emphasizing the high variability of these amino acid positions. Codon 481 was mutated on 32 separate occasions, which indicates a central role of this amino acid. All in vivo isolates that demonstrated two or three amino acid changes exhibited high-level resistance. Interestingly enough, all of these isolates showed the mutational change 481His-Asn, which is capable of conferring low-level resistance on its own, thereby indicating a two-step resistance mechanism in vivo to high-level resistance within these isolates. High-level resistance in vivo, however, was not demonstrated to occur through multiple mutations alone. The single amino acid substitution 468Gln-Lys also causes high-level resistance. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
