Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00059) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Pefloxacin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Abactal; Labocton; PERFLOXACIN; PFLX; Peflacine; Pefloxacine; Pefloxacino; Pefloxacinum; Pefloxacin methanesulfonate; Silver Pefloxacin; AM-725; EU-5306; Pefloxacin [INN-French]; Pefloxacino [INN-Spanish]; Pefloxacinum [INN-Latin]; Pefloxacin (USAN/INN); Pefloxacin [USAN:BAN:INN]; 1-Ethyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid; 1-Ethyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-7-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid; 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-7-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid; 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-7-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid; 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-7-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid; 3-Quinolinecarboxylic acid, 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-7-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-4-oxo
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
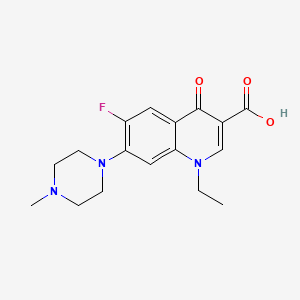
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(2 diseases)
[2]
[1]
|
||||
| Target | DNA topoisomerase II (TOP2) |
TOP2A_HUMAN
; TOP2B_HUMAN |
[1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C17H20FN3O3
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CCN1C=C(C(=O)C2=CC(=C(C=C21)N3CCN(CC3)C)F)C(=O)O
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C17H20FN3O3/c1-3-20-10-12(17(23)24)16(22)11-8-13(18)15(9-14(11)20)21-6-4-19(2)5-7-21/h8-10H,3-7H2,1-2H3,(H,23,24)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
FHFYDNQZQSQIAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-12: Respiratory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: DNA topoisomerase 4 subunit A (PARC) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pneumocystis jirovecii infection [ICD-11: CA40.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D84H (GAT-CAT) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Streptococcus pneumoniae strain BM4203-BM4203-R | 1313 | ||
| Streptococcus pneumoniae strain BM4204-BM4204-R | 1313 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sequence analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mutations in parC were detected in the two resistant mutants obtained in vivo (BM4203-R andBM4204-R) as well as in two (BM4203-R1 and BM4203-R2) of the six mutants obtained in vitro. These mutations led to Ser-80-Tyr or Phe or to Asp-84-His substitutions(S. aureus coordinates) that are either identical or similar to those found in low-level-resistant parC mutations of S. aureus:Ser-80-Tyr or Phe and Glu-84-Lys or Leu. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA topoisomerase 4 subunit A (PARC) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pneumocystis jirovecii infection [ICD-11: CA40.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S80Y (TCT-TAT) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Streptococcus pneumoniae strain BM4203-BM4203-R | 1313 | ||
| Streptococcus pneumoniae strain BM4204-BM4204-R | 1313 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sequence analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mutations in parC were detected in the two resistant mutants obtained in vivo (BM4203-R andBM4204-R) as well as in two (BM4203-R1 and BM4203-R2) of the six mutants obtained in vitro. These mutations led to Ser-80-Tyr or Phe or to Asp-84-His substitutions(S. aureus coordinates) that are either identical or similar to those found in low-level-resistant parC mutations of S. aureus:Ser-80-Tyr or Phe and Glu-84-Lys or Leu. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA topoisomerase 4 subunit A (PARC) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pneumocystis jirovecii infection [ICD-11: CA40.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S80F (TCT-TTT) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Streptococcus pneumoniae strain BM4203-BM4203-R | 1313 | ||
| Streptococcus pneumoniae strain BM4204-BM4204-R | 1313 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sequence analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mutations in parC were detected in the two resistant mutants obtained in vivo (BM4203-R andBM4204-R) as well as in two (BM4203-R1 and BM4203-R2) of the six mutants obtained in vitro. These mutations led to Ser-80-Tyr or Phe or to Asp-84-His substitutions(S. aureus coordinates) that are either identical or similar to those found in low-level-resistant parC mutations of S. aureus:Ser-80-Tyr or Phe and Glu-84-Lys or Leu. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: DNA gyrase subunit A (GYRA) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pneumocystis jirovecii infection [ICD-11: CA40.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S843F (TCC-TTC) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Streptococcus pneumoniae strain BM4203-BM4203-R | 1313 | ||
| Streptococcus pneumoniae strain BM4204-BM4204-R | 1313 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sequence analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | An additional mutant obtained in vitro, BM4205-R3, displayed a higher level of fluoroquinolone resistance and had a mutation in gyrA leading to a Ser-84-Phe change. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
