Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00009) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Pulvomycin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Pulvomycin; AC1NQZFA; C12070; 11006-66-9; CHEBI:29668
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
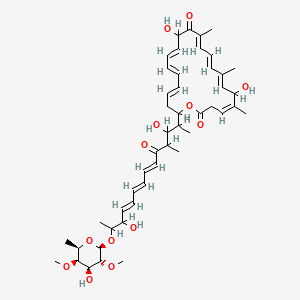
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C47H66O13
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C[C@@H]1[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H](O1)OC(C)C(/C=C/C=C/C=C/C(=O)C(C)C(C(C)C2C/C=C/C=C/C=C/C(C(=O)/C(=C/C=C/C(=C/C(/C(=C\\CC(=O)O2)/C)O)/C)/C)O)O)O)OC)O)OC
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C47H66O13/c1-29-20-19-21-31(3)42(53)38(50)24-17-11-10-12-18-25-40(60-41(52)27-26-30(2)39(51)28-29)33(5)43(54)32(4)36(48)22-15-13-14-16-23-37(49)34(6)58-47-46(57-9)44(55)45(56-8)35(7)59-47/h10-24,26,28,32-35,37-40,43-47,49-51,54-55H,25,27H2,1-9H3/b11-10+,14-13+,18-12+,20-19+,22-15+,23-16+,24-17+,29-28+,30-26-,31-21+/t32 ,33 ,34 ,35-,37 ,38 ,39 ,40 ,43 ,44+,45+,46-,47-/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
FXSFWUNCIOIMAC-YHQXOMPPSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Elongation factor Tu 1 (TUFA) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R230C |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain LZ33L | 562 | ||
| Escherichiacoli strain EV4 | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LBE2040 | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LZ32L | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LZ35L | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LZ36L | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LZ37L | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain MG1655 | 511145 | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Together with targeted mutagenesis of the tufA gene, conditions were found to overcome membrane impermeability, thereby allowing the selection of three mutants harbouring elongation factor (EF)-Tu Arg230-->Cys, Arg333-->Cys or Thr334-->Ala which confer pulvomycin resistance.Pulvomycin and kirromycin both act by specifically disturbing the allosteric changes required for the switch from EF-Tu-GTP to EF-Tu-GDP. The three-domain junction changes dramatically in the switch to EF-Tu.GDP; in EF-Tu.GDP this region forms an open hole. The two most highly resistant mutants, R230C and R333C, are part of an electrostatic network involving numerous residues. | |||
| Key Molecule: Elongation factor Tu 2 (TUFB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R230C |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain LZ33L | 562 | ||
| Escherichiacoli strain EV4 | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LBE2040 | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LZ32L | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LZ35L | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LZ36L | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LZ37L | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain MG1655 | 511145 | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Together with targeted mutagenesis of the tufA gene, conditions were found to overcome membrane impermeability, thereby allowing the selection of three mutants harbouring elongation factor (EF)-Tu Arg230-->Cys, Arg333-->Cys or Thr334-->Ala which confer pulvomycin resistance.Pulvomycin and kirromycin both act by specifically disturbing the allosteric changes required for the switch from EF-Tu-GTP to EF-Tu-GDP. The three-domain junction changes dramatically in the switch to EF-Tu.GDP; in EF-Tu.GDP this region forms an open hole. The two most highly resistant mutants, R230C and R333C, are part of an electrostatic network involving numerous residues. | |||
| Key Molecule: Elongation factor Tu 1 (TUFA) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R333C |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain LZ33L | 562 | ||
| Escherichiacoli strain EV4 | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LBE2040 | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LZ32L | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LZ35L | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LZ36L | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LZ37L | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain MG1655 | 511145 | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Together with targeted mutagenesis of the tufA gene, conditions were found to overcome membrane impermeability, thereby allowing the selection of three mutants harbouring elongation factor (EF)-Tu Arg230-->Cys, Arg333-->Cys or Thr334-->Ala which confer pulvomycin resistance.Pulvomycin and kirromycin both act by specifically disturbing the allosteric changes required for the switch from EF-Tu-GTP to EF-Tu-GDP. The three-domain junction changes dramatically in the switch to EF-Tu.GDP; in EF-Tu.GDP this region forms an open hole. The two most highly resistant mutants, R230C and R333C, are part of an electrostatic network involving numerous residues. | |||
| Key Molecule: Elongation factor Tu 2 (TUFB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R333C |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain LZ33L | 562 | ||
| Escherichiacoli strain EV4 | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LBE2040 | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LZ32L | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LZ35L | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LZ36L | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LZ37L | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain MG1655 | 511145 | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Together with targeted mutagenesis of the tufA gene, conditions were found to overcome membrane impermeability, thereby allowing the selection of three mutants harbouring elongation factor (EF)-Tu Arg230-->Cys, Arg333-->Cys or Thr334-->Ala which confer pulvomycin resistance.Pulvomycin and kirromycin both act by specifically disturbing the allosteric changes required for the switch from EF-Tu-GTP to EF-Tu-GDP. The three-domain junction changes dramatically in the switch to EF-Tu.GDP; in EF-Tu.GDP this region forms an open hole. The two most highly resistant mutants, R230C and R333C, are part of an electrostatic network involving numerous residues. | |||
| Key Molecule: Elongation factor Tu 1 (TUFA) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T334A |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain LZ33L | 562 | ||
| Escherichiacoli strain EV4 | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LBE2040 | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LZ32L | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LZ35L | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LZ36L | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LZ37L | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain MG1655 | 511145 | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Together with targeted mutagenesis of the tufA gene, conditions were found to overcome membrane impermeability, thereby allowing the selection of three mutants harbouring elongation factor (EF)-Tu Arg230-->Cys, Arg333-->Cys or Thr334-->Ala which confer pulvomycin resistance.Pulvomycin and kirromycin both act by specifically disturbing the allosteric changes required for the switch from EF-Tu-GTP to EF-Tu-GDP. The three-domain junction changes dramatically in the switch to EF-Tu.GDP; in EF-Tu.GDP this region forms an open hole. The two most highly resistant mutants, R230C and R333C, are part of an electrostatic network involving numerous residues. | |||
| Key Molecule: Elongation factor Tu 2 (TUFB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T334A |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain LZ33L | 562 | ||
| Escherichiacoli strain EV4 | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LBE2040 | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LZ32L | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LZ35L | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LZ36L | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain LZ37L | 562 | |||
| Escherichiacoli strain MG1655 | 511145 | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Together with targeted mutagenesis of the tufA gene, conditions were found to overcome membrane impermeability, thereby allowing the selection of three mutants harbouring elongation factor (EF)-Tu Arg230-->Cys, Arg333-->Cys or Thr334-->Ala which confer pulvomycin resistance.Pulvomycin and kirromycin both act by specifically disturbing the allosteric changes required for the switch from EF-Tu-GTP to EF-Tu-GDP. The three-domain junction changes dramatically in the switch to EF-Tu.GDP; in EF-Tu.GDP this region forms an open hole. The two most highly resistant mutants, R230C and R333C, are part of an electrostatic network involving numerous residues. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
